IgG in patients with tuberculosis inhibits intracellular bacteria
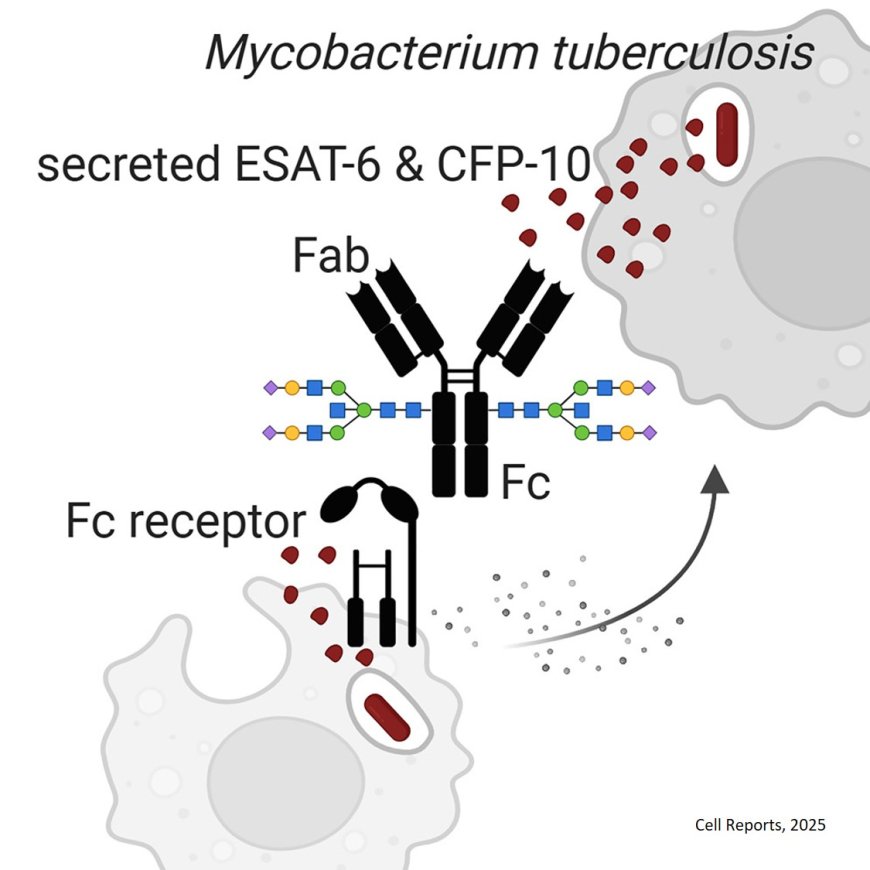
Antibodies represent a well-established arm of immunity in many infectious diseases, but their role in tuberculosis is underappreciated.
This study identifies key characteristics of polyclonal antibodies (IgG) in human TB that target the mycobacterial virulence factors ESAT-6 and CFP-10 and restrict intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis, showing the potential for humoral immunity to protect.
The authors show that IgG glycosylation and Fc-Fc receptor binding enable antibody-mediated anti-Mtb activities.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)01425-1
https://sciencemission.com/IgG-in-patients-with-tuberculosis