Improving base editing efficiency for disease correction
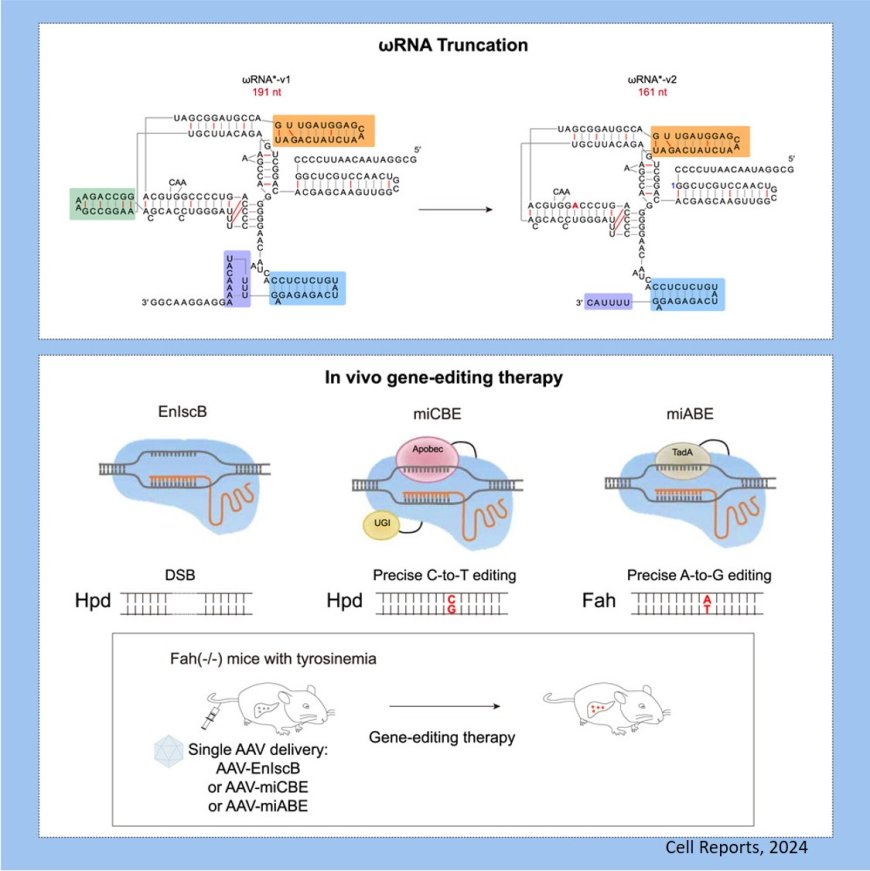
IscBs are proteins of Cas9 nuclease and have been used for in vivo gene editing via single adeno-associated virus (AAV) delivery but with a low activity. Researchers have been trying to increase the efficiency of IscBs.
They engineered an IscB-associated uRNA variant, uRNA* -v2, of the transposon-encoded OMEGA system to enhance gene knockout and cytosine and adenine base editing activity in human cells and to correct disease-causing mutations in a disease mouse model via single AAV in vivo delivery.
The researchers demonstrated that single AAV delivery of IscB-derived cytosine and adenine base editors achieved disease correction in a mouse model of tyrosinemia.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01324-X