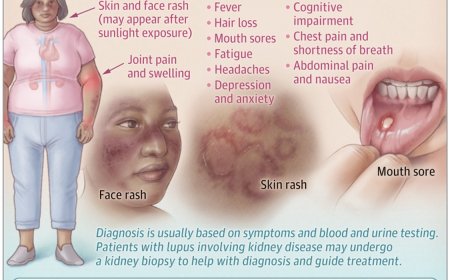
Microglial cGAS Deletion Alleviates Amyloid-β-Induced Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease
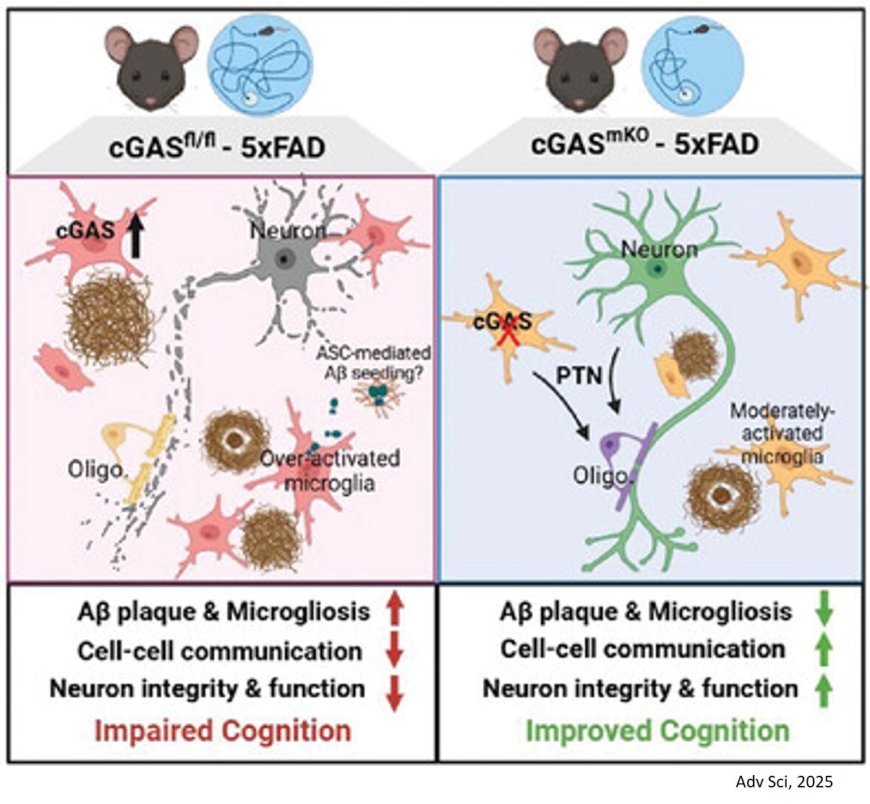
Innate immune activation and cytosolic DNA sensing pathway involving cGAMP synthase (cGAS) and Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) are linked to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and related dementias (ADRD).
But, the mechanisms through which cGAS activation influences AD progression remain poorly understood.
The researchers demonstrate significant up-regulation of cGAS-STING signaling pathway in microglia in AD.
In cGAS knockout mouse model restricted plaque accumulation and protected mice from Aβ-induced cognitive impairment.
The authors show that cGAS promoted plaque-associated microglia accumulation and inflammasome activation and . restricting cGAS-mediated innate immunity is crucial for preserving inter-cellular communication in the brain and induces pleiotrophin, a neuroprotective factor.
https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/advs.202410910