Analysis of CreutzfeldtJakob disease risk genes
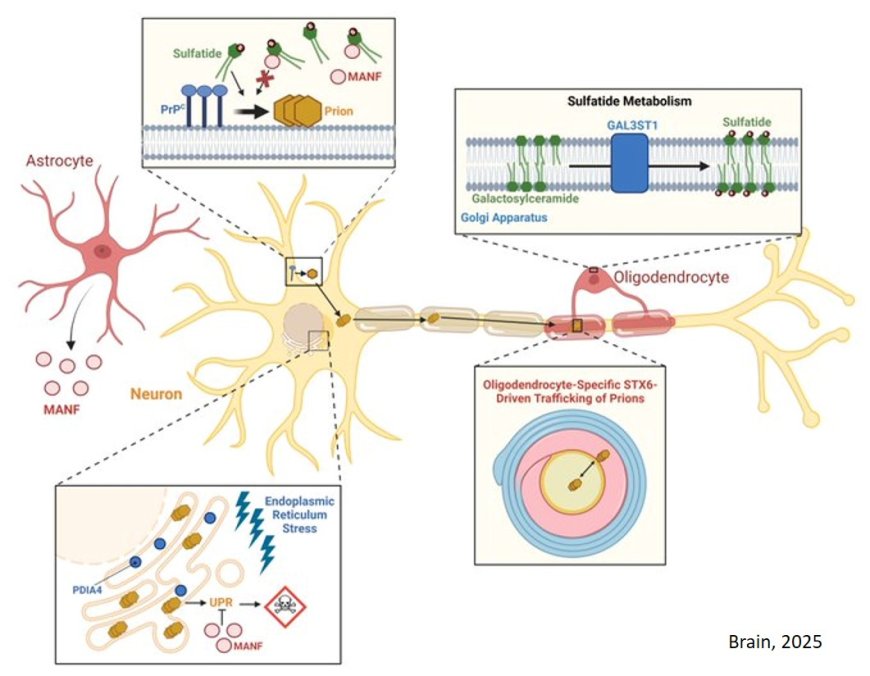
The researchers integrate GWAS data with transcriptome and proteome-wide association studies to better understand risk factors for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, the most common human prion disease.
The authors identified oligodendrocyte specific genetic upregulation of both gene and protein expression of syntaxin-6 (STX6) in the brain as a risk factor.
Another risk factor was found in excitatory neurons the authors, where in, increased gene and protein expression of protein disulfide isomerase family A member 4 (PDIA4), involved in the unfolded protein response.
Protein expression of mesencephalic astrocyte derived neurotrophic factor (MANF), involved in protection against endoplasmic reticulum stress and sulfatide binding was identified as protective.
https://academic.oup.com/brain/advance-article/doi/10.1093/brain/awaf032/7981667
https://sciencemission.com/Creutzfeldt--Jakob-disease-risk-genes