Molecular mechanisms of the mammalian fatty acid cycle
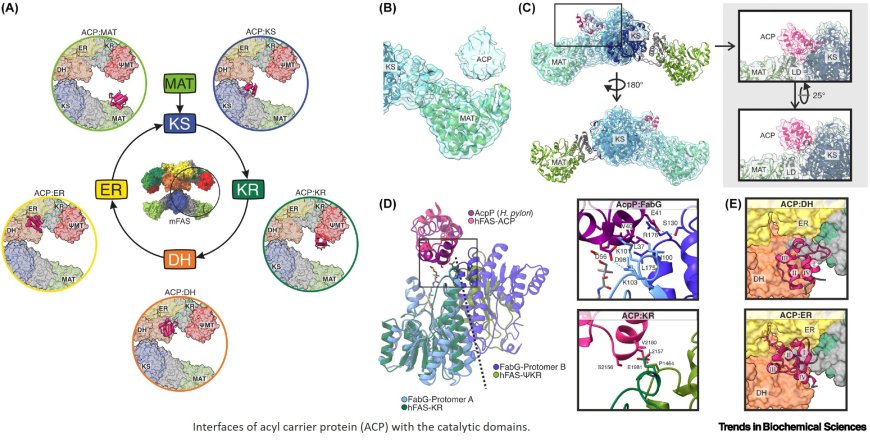
The mammalian fatty acid synthase (mFAS) is an enzyme complex that performs de novo fatty acid biosynthesis in an iterative cycle.
The complex utilizes substrate shuttling, which is executed by the acyl carrier protein (ACP) that transfers the substrate to the six catalytic domains of the complex.
In contrast to previous models, recent studies show that large conformational dynamics are considerably less relevant for the efficiency of mFAS.
These studies also show that the ACP:domain interactions are governed by the interface area and charge complementarity.
https://www.cell.com/trends/biochemical-sciences/fulltext/S0968-0004(25)00223-3












