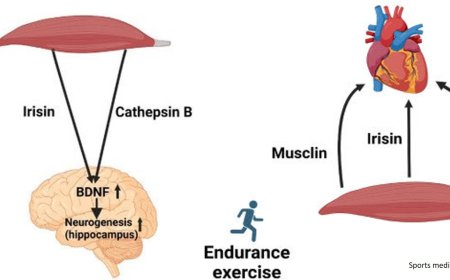
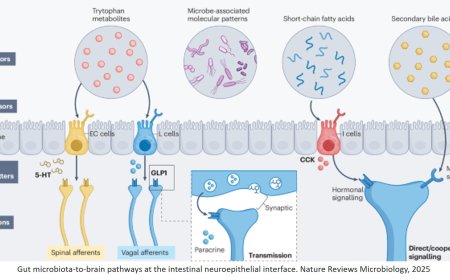
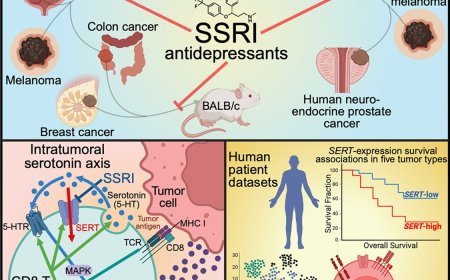
Neuronal polyunsaturated fatty acids are protective in ALS/FTD
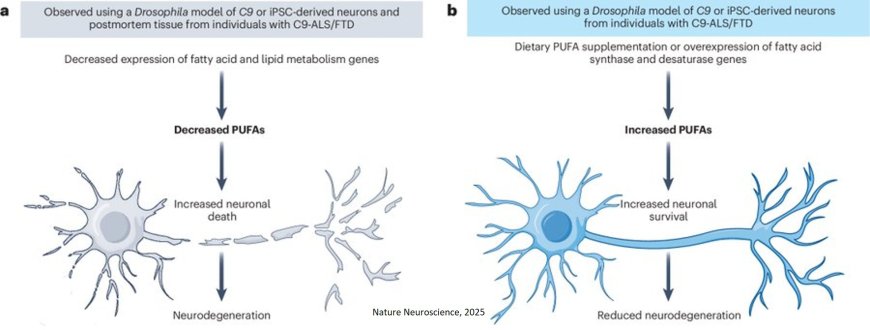
C9orf72 gene repeat expansion is the the most common genetic cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (ALS/FTD).
In a Drosophila model and in induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell neurons and postmortem FTD brain tissue, the researchers show reduced fatty acid and lipid metabolism gene expression especially polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
When C9 ALS/FTD flies were fed PUFAs, a modest increase in survival but overexpressing fatty acid desaturase enzymes that increase PUFA levels in neurons of C9 ALS/FTD fies, led to a substantial extension of lifespan.
Neuronal overexpression of fatty acid desaturases also suppressed stressor-induced neuronal death in iPS cell neurons of patients with both C9 and TDP-43 ALS/FTD.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-01889-3
https://sciencemission.com/Neuronal-PUFA-are-protective-in-ALS