Neuronal autophagy in the control of synapse function
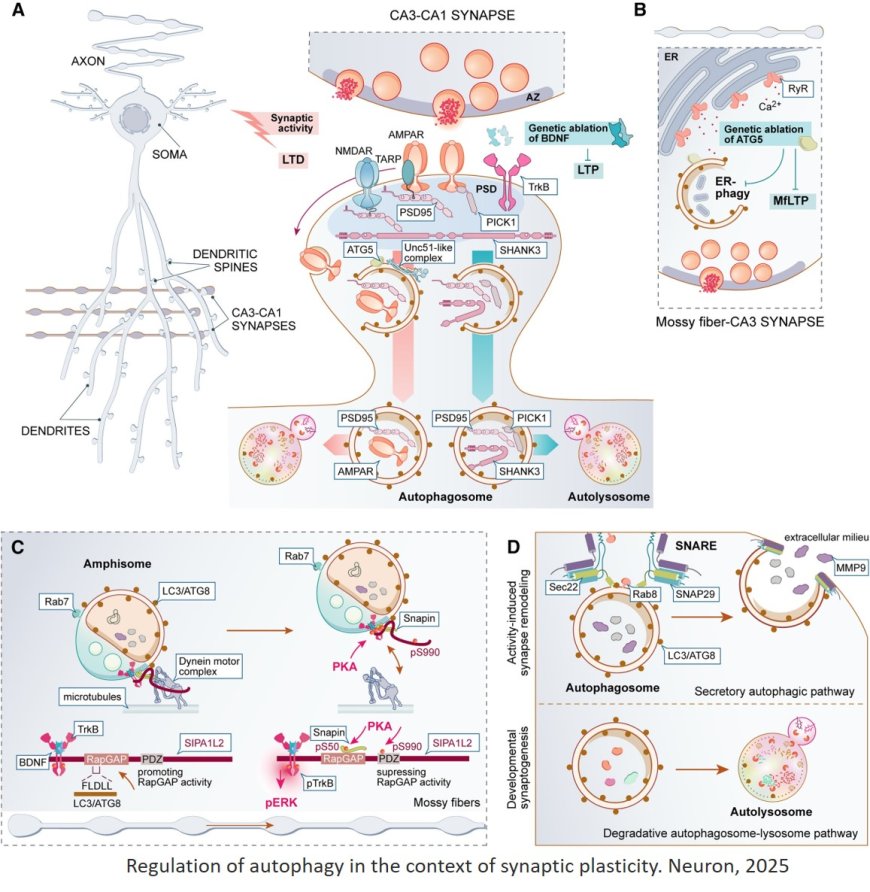
In neurons, autophagy removes toxic or defective proteins and organelles and maintains neurotransmission and the integrity of their functional proteome.
Epilepsy, intellectual disability, and neurodegeneration have been linked to mutations in autophagy genes.
Motor deficits, memory impairment, altered sociability, and epilepsy are associated ablation of core autophagy genes in neurons or glia.
The substrates of neuronal autophagy and the mechanisms by which defects in autophagy affect synaptic function in health and disease remain less understood.
The researchers summarize the current state of knowledge on neuronal autophagy, address the existing controversies and inconsistencies in the field, and provide a roadmap for future research on the role of autophagy in the control of synaptic function.