Opposing roles for AMPK in regulating distinct mitophagy pathways
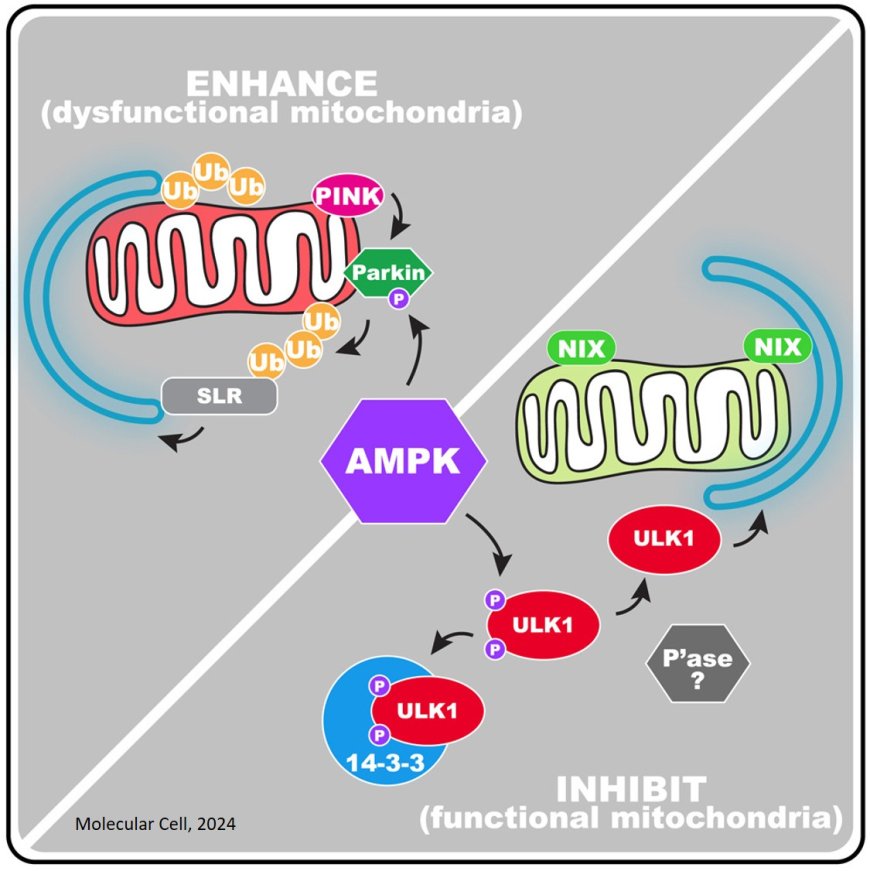
Under energetic stress, it is essential to balance dysfunctional versus healthy mitochondrial turnover. Damaged mitochondria are removed by mitophagy but functional mitochondria are also degraded sometimes by programmed mitophagy and involves the mitophagy receptors NIX and BNIP3.
The researchers uncover a mechanism by which AMPK activation achieves this programmed mitophagy.
They find that although AMPK enhances Parkin-mediated mitophagy upon mitochondrial damage, it blocks NIX-mediated mitophagy, which they now show can target functioning mitochondria.
Mechanistically, the researchers found that AMPK directly inhibits NIX-dependent mitophagy by triggering 14-3-3-mediated sequestration of ULK1, via ULK1 phosphorylation at two sites. By contrast, AMPK activation increases Parkin phosphorylation and enhances the rate of depolarization-induced mitophagy, independently of ULK1.
https://www.cell.com/molecular-cell/fulltext/S1097-2765(24)00865-7
https://sciencemission.com/Opposing-roles-for-AMPK-in-regulating-distinct-mitophagy-pathways