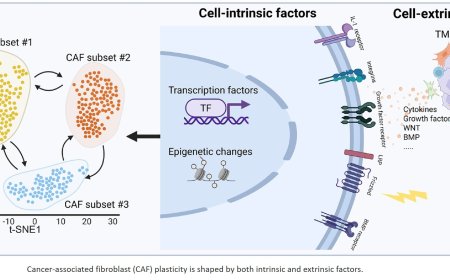
A heart-brain-spleen axis controls cardiac remodeling to hypertensive stress
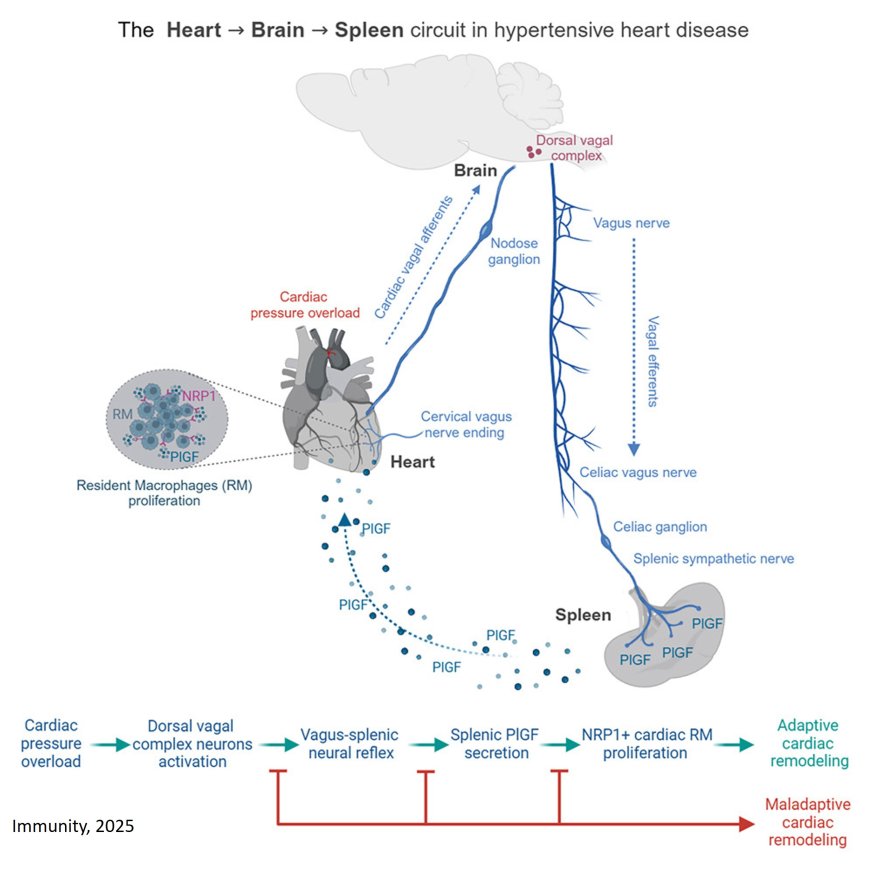
Hypertensive heart disease, initially established as an adaptive response, might progress toward heart failure, and the nervous and immune systems participate in this process, but their interaction is unclear.
The authors show that during stress, recruitment of a brainstem neural circuit to enhance splenic sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and induce placental growth factor (PlGF) secretion and PlGF drove the proliferation of self-renewing cardiac resident macrophages (RMs) expressing its receptor neuropilin-1 (NRP1).
Inhibition of the splenic neuroimmune axis or ablation of NRP1 in RM hindered the adaptive response to hypertensive stress, leading to heart failure.
In humans, circulating PlGF correlated with cardiac hypertrophy, and failing hearts expressed NRP1 in RMs.
https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(25)00080-9