Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and their hydrolases
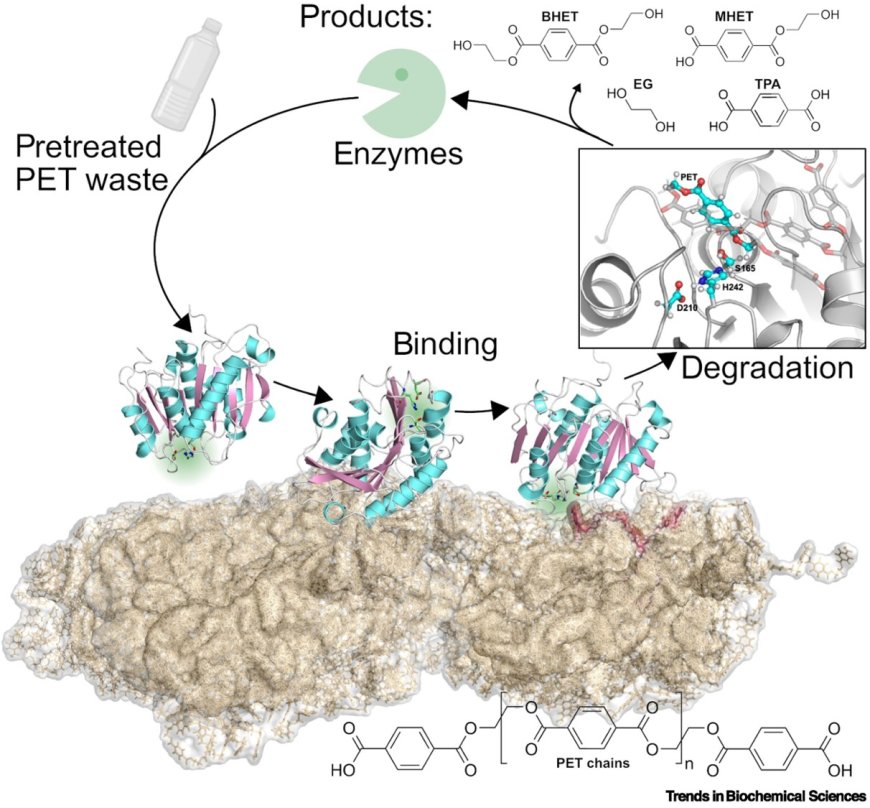
The existence of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) hydrolases is striking, given that PET is a synthetic polymer and enzymes evolved for natural substrates.
To enhance the applicability of PET hydrolases in industrial settings, targeted enzyme reengineering is essential.
Strategies for improving PET hydrolases include increasing thermostability, accelerating catalytic reactions, and optimizing binding to PET substrates. According to the Sabatier principle, achieving optimal binding strength between PET and PET hydrolases is crucial for effective catalysis.
A range of biochemical and biophysical techniques is available to enhance our understanding of PET hydrolase adsorption to PET, paving the way for advanced enzyme design.
https://www.cell.com/trends/biochemical-sciences/fulltext/S0968-0004(25)00106-9