PIEZO channels in mechanotransduction
In mammals mechanical forces are sensed and transduced into biological activities via evolutionarily conserved PIEZO family of proteins including PIEZO1 and PIEZO2.
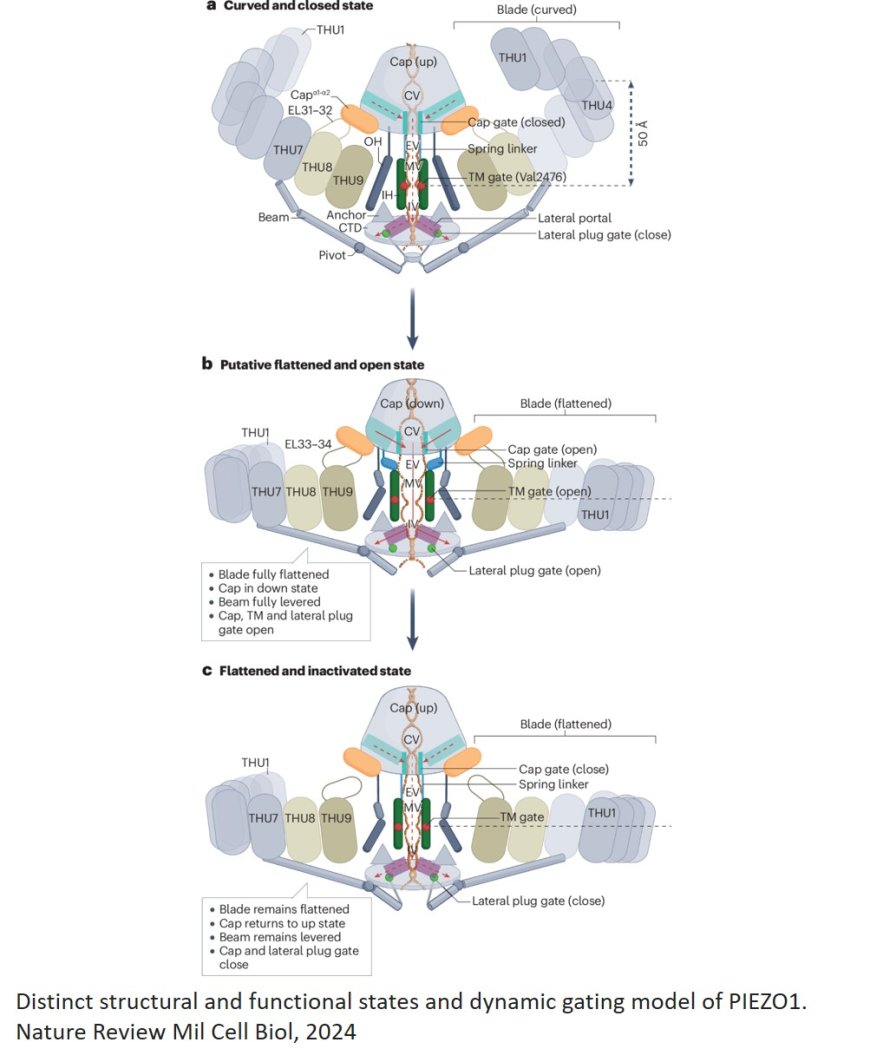
In this review, the researchers discuss unique structural design and curvature-based gating dynamics of PIEZO channels, enabling their function as dedicated mechanotransduction channels with high mechanosensitivity and selective cation conductivity.
The researchers also discuss physiological and pathophysiological roles mediated by PIEZO channels, including PIEZO1-dependent regulation of development and functional homeostasis and PIEZO2-dominated mechanosensation of touch, tactile pain, proprioception and interoception of mechanical states of internal organs.