Role of parathymosin (PTMS) in aging-associated neurodegeneration
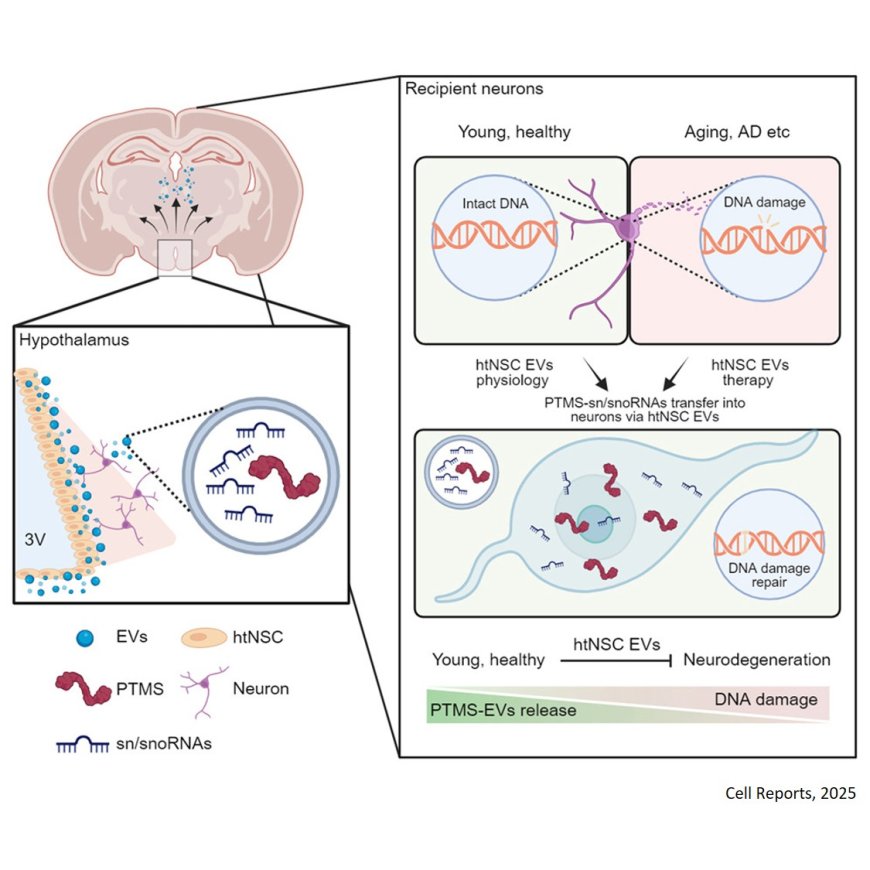
Parathymosin (PTMS), a secretory protein with nuclear functions, has recently been identified as a circulating factor in the brain.
The researchers reveal a critical neuroprotective role of PTMS, while loss of this protein causes severe neurodegeneration and reduced lifespan. .
PTMS is present in hypothalamic extracellular vesicles (EVs), particularly in subpopulations released by hypothalamic neural stem/progenitor cells.
Hypothalamic neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles carrying PTMS protect neurons by preventing DNA damage and offer therapeutic benefits against aging=related neurodegenerative and Alzheimer’s-like conditions in animal models.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)01333-6
https://sciencemission.com/aging-associated-neurodegeneration