Sickle cell disease pain from gut dysbiosis
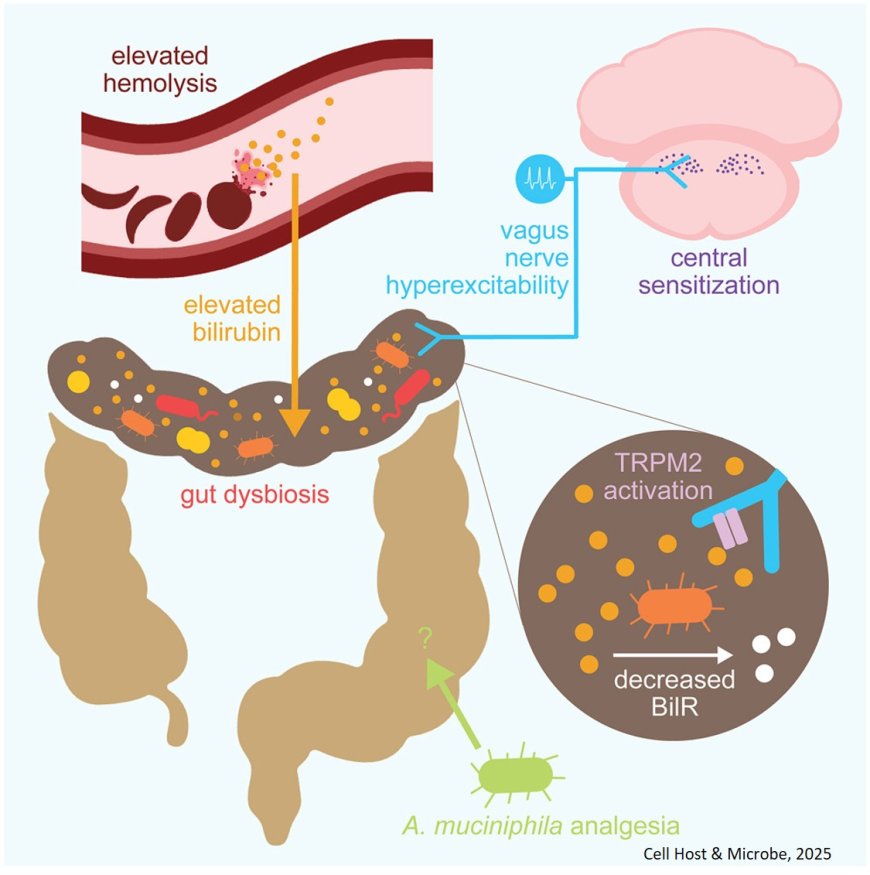
The mechanism of chronic pain from sickle cell disease (SCD) is not well understood.
The researchers revealed gut dysbiosis in individuals with SCD and describe how the gut microbiome drives chronic sickle cell disease (SCD) pain.
They show that SCD guts contain excessive heme catabolites, fewer bacteria that metabolize bilirubin, and low levels of Akkermansia muciniphila. Elevated intestinal bilirubin drives pain by activating TRPM2 on vagal afferents.
Addition of A. muciniphila or treatment with TRPM2 inhibitors—which block bilirubin-induced vagus nerve activity— alleviate SCD pain.
https://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(25)00338-5