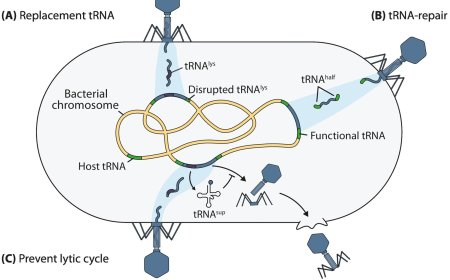
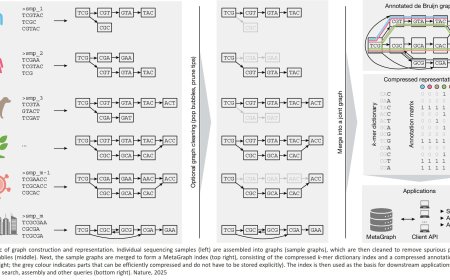
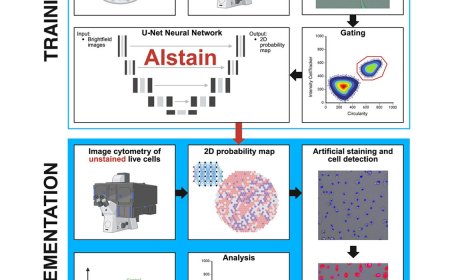
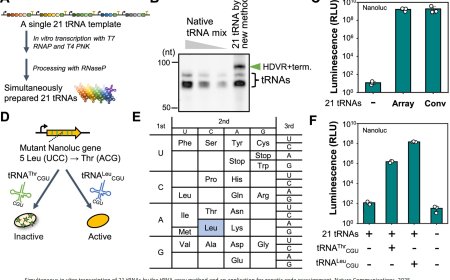
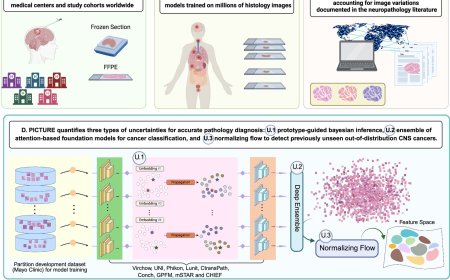
Salmonella elimination by commensal E. coli during intestinal inflammation
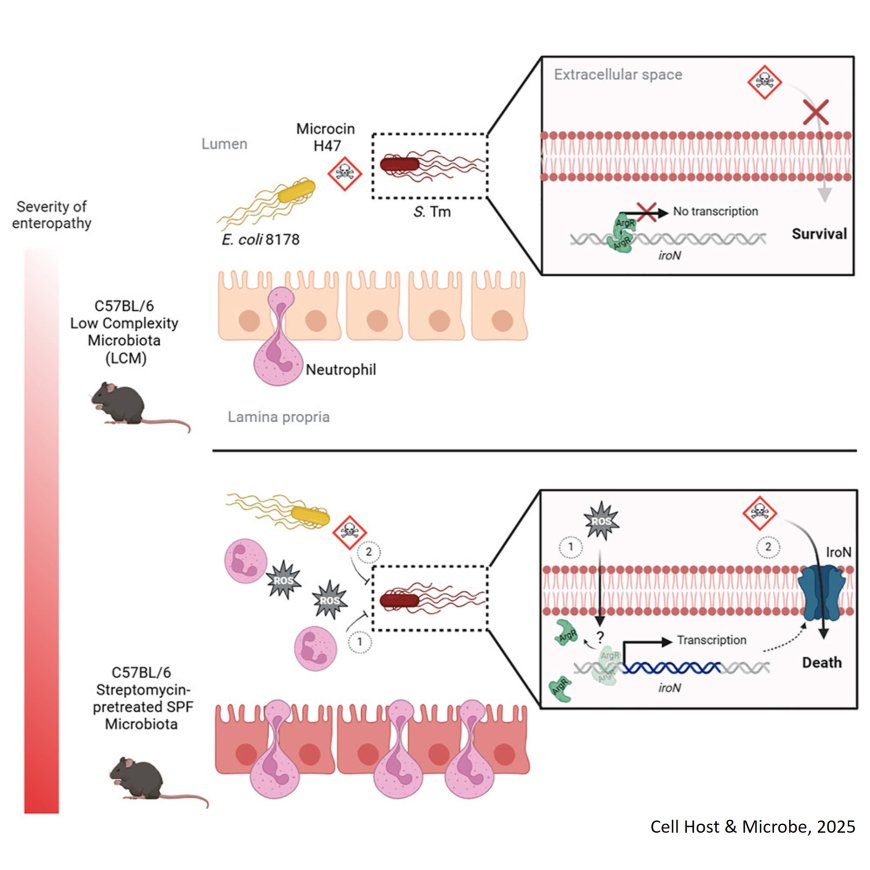
How intestinal microbiota interacts with pathogen during food poisoning and protects the host is not clearly understood.
The researchers found that reduction of gut luminal Salmonella Typhimurium by protective commensal E. coli strains depends on the degree of intestinal inflammation.
Severe gut inflammation is followed by recruitment of intraluminal neutrophils, which make Salmonella vulnerable to toxin-producing protective E. coli strains.
https://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(25)00052-6
https://sciencemission.com/intestinal-inflammation-Salmonella--E-coli