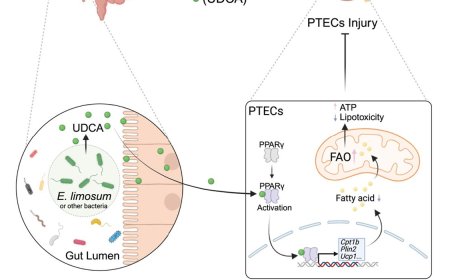
Synthetic 3D extracellular matrix for muscle tissue
Extracellular matrix (ECM) plays an important role in cellular proliferation, migration and differentiation and 3D matrix that represents ECM has been developed for research and therapeutic purposes to grow and differentiate cells.
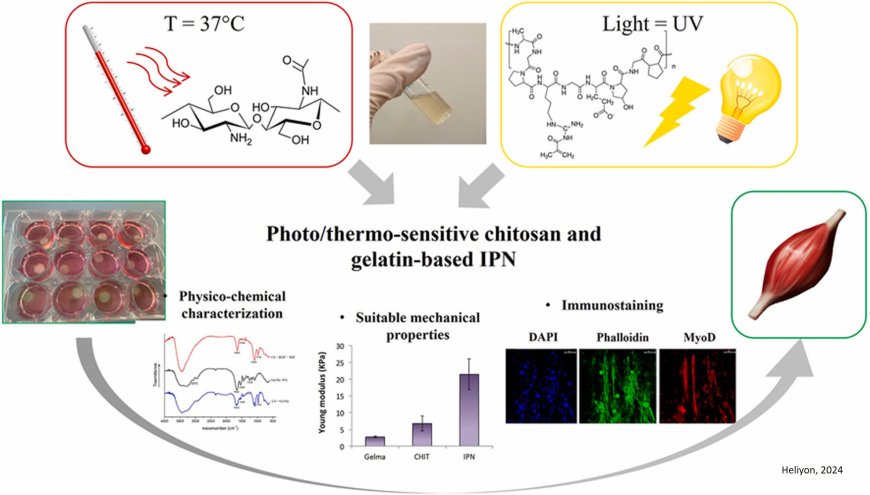
In this study, the researchers used chitosan and methacrylated gelatin to create a dual-sensitive hydrogel. These interpenetrating polymer networks (IPN) were injectable, stable and sensitive to both light and temperature.
The authors show that IPN mechanical properties resemble those of muscle tissues and supported C2C12 differentiation toward a muscle phenotype.
The authors believe that the system represents a suitable 3D model for investigating neuromuscular diseases.