Tumor-induced metabolic immunosuppression
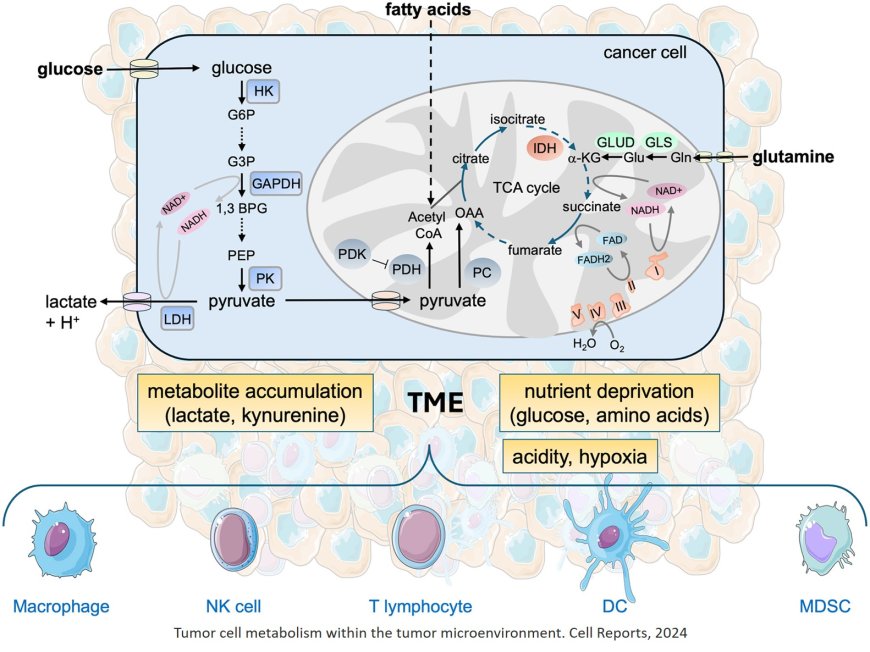
Cancer metabolism is modulated during tumorigenesis that helps in the survival of tumor cells via altered signaling but also modulates immune cell function.
Metabolic crosstalk within the tumor microenvironment results in nutrient competition and acidosis, thereby hindering immune cell functionality. Immune cells also undergo metabolic reprogramming that enables their proliferation, differentiation, and effector functions.
In this review, the authors highlight the regulation of antitumor immune responses through metabolic reprogramming in cancer and immune cells.
They explore therapeutic strategies that target these metabolic pathways in cancer immunotherapy, including using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells.
They also discuss combination therapies involving immunotherapy, cellular, and metabolic interventions that could optimize the efficacy of existing treatment protocols.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01557-2
https://sciencemission.com/Tumor-induced-metabolic-immunosuppression