How exercise-driven gut microbiota protects against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
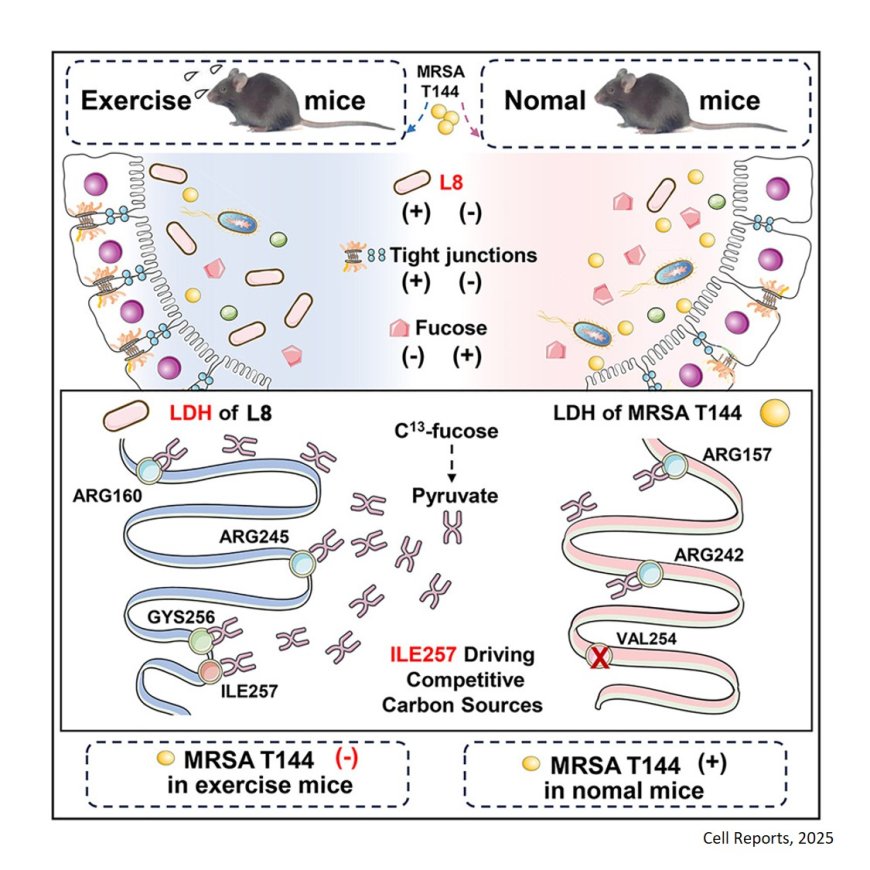
Gut-microbiota-mediated colonization resistance plays a vital role in protecting against invading pathogens.
Although exercise offers numerous health benefits, its role in host colonization resistance remains largely unclear.
The researchers reveal the importance of moderate exercise-driven gut microbiota alterations in maintaining host colonization resistance, as evidenced by significantly reduced gut colonization by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a clinically important MDR pathogen.
The authors show that probiotic strain L8 outcompetes MRSA through a microbiome-based nutrient depletion strategy.
Mechanistically, they demonstrate that intestinal probiotic Dubosiella newyorkensis (L8) act as a critical factor in mediating exercise-induced colonization resistance against MRSA by enhancing the deprivation of fucose, a crucial carbon source essential for MRSA growth and pathogenicity.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00195-0