Interactions between sex hormones and neurological health
A comprehensive review published in Brain Medicine maps out the extensive influence of reproductive hormones on neurological health and disease. This landmark review, systematically examines how sex hormones affect a broad spectrum of neurological conditions.
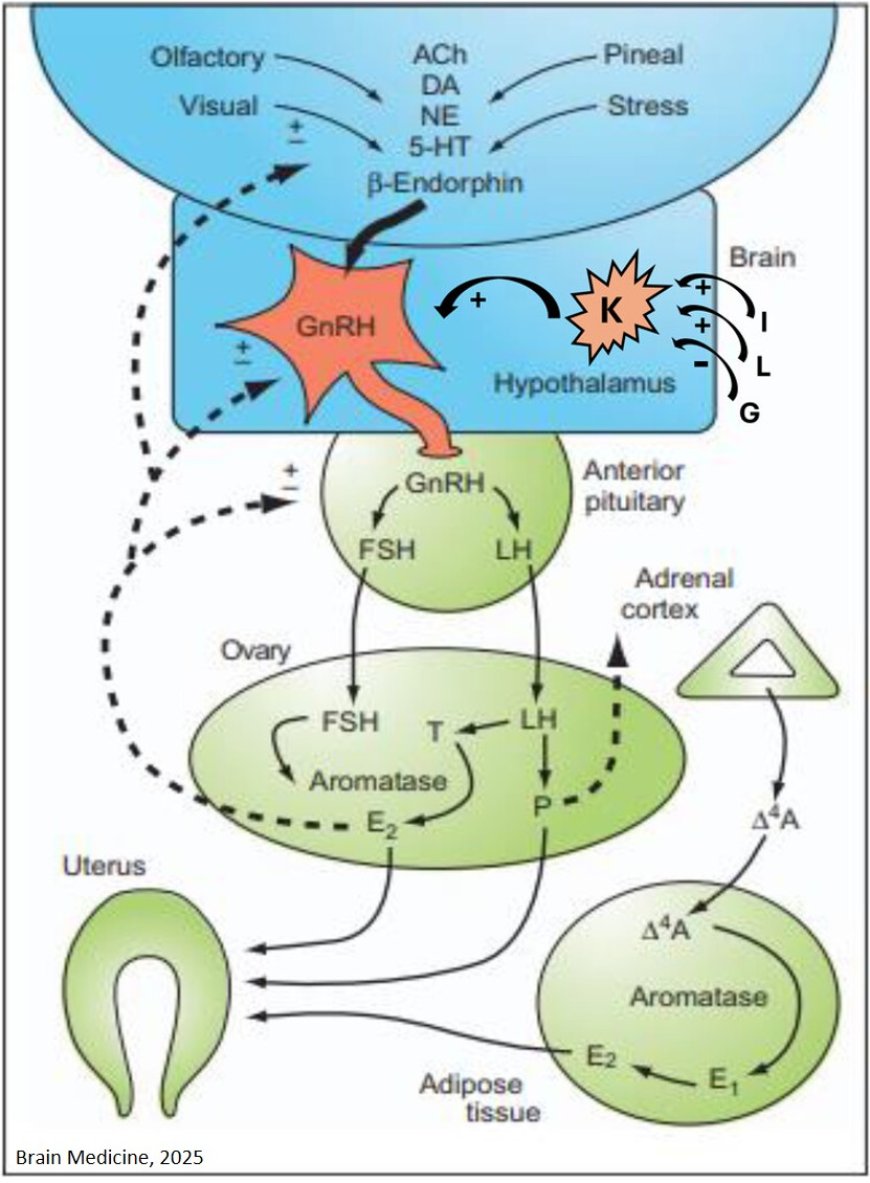
The review details how sex hormones influence neurological function through multiple mechanisms, including direct effects on nerve cells, epigenetic modifications, and the newly discovered brain glymphatic system. The analysis covers an extensive range of conditions, including:
• Vascular disorders such as migraine (affecting up to 60% of female sufferers during menstruation) and stroke
• Movement disorders, particularly Parkinson’s disease, Wilson’s disease, and various forms of chorea
• Epilepsy, especially its relationship with hormonal cycles
• Multiple sclerosis, which often shows distinct patterns during pregnancy
• Alzheimer’s disease and its complex relationship with hormonal factors
• Sleep disorders, which show significant gender-based differences
• Brain tumors, particularly hormone-sensitive meningiomas
• Neuromuscular conditions like myasthenia gravis
• Other conditions, including intracranial hypertension and the porphyrias
“Our understanding of how reproductive hormones impact neurological conditions has expanded dramatically,” explains the author. “These hormones don’t just affect reproductive functions - they fundamentally influence how the nervous system develops, functions, and responds to injury or disease.”
The review highlights several key findings:
• induction of the cytochrome P450 system in the liver by various anti-epileptic and other neurological pharmaceuticals may accelerate the breakdown of circulating sex steroids resulting in oral contraceptive failure
• Neurosteroids, which are hormone-derived molecules produced in the brain, have significant therapeutic potential
• Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can substantially impact disease manifestation and treatment responses
• Sex-specific approaches may be necessary for treating many neurological conditions
The research raises important questions for future investigation, including:
• How do sex hormones interact with the brain’s waste clearance (glymphatic) system?
• Could targeting neurosteroid pathways offer new therapeutic approaches?
• How might hormone-based treatments be optimized for individual patients?
These findings have significant implications for clinical practice, suggesting neurologists should routinely consider hormonal factors when evaluating and treating patients. “The key is understanding exactly how these hormones work in different contexts,” notes the author. “This knowledge could lead to more personalized treatment approaches.”