Microfluidic systems resembling blood vascular tissues
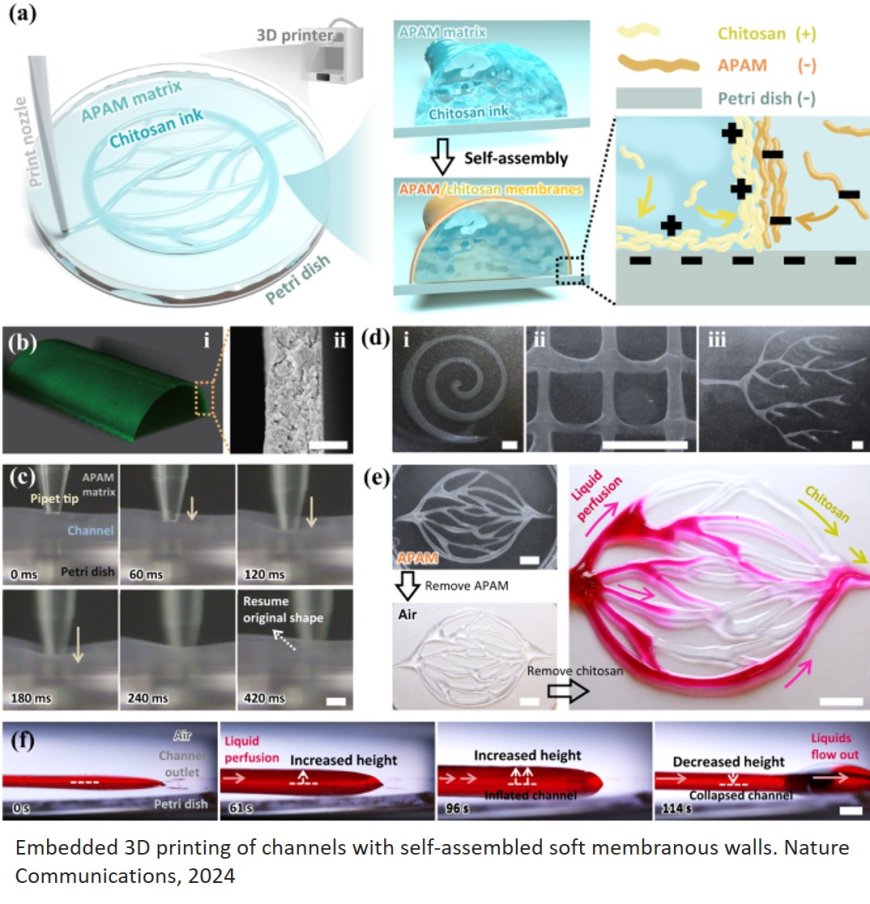
The fluidic system can modulate fluid compositions via spatially-different reactions between fluids and channel walls, something that has not yet been realised in traditional fluidic systems. This work was conducted by the research team has been published in Nature Communications.
"The brilliant control over blood compositions in vessels is remarkable and essential, inspiring us to think about how to design new fluidic systems," shared the first author of the research project.
The blood vascular network, a natural fluidic system, inspired the research. "Guided" by the vascular network, the team developed VasFluidics, a fluidic system with functionalisable membrane walls. Similar to blood vessel walls, the walls of VasFluidic channels are thin, soft, and capable of changing liquid compositions via physical or chemical means.
This study demonstrates the power of VasFluidics in fluid processing. After separated channel regions are deposited with solutions or coated with enzymes, some regions of the VasFluidic channels physically allow specific molecules to pass through the channel walls, while some chemically change liquid compositions. The results are reminiscent of glucose adsorption and metabolism processes in the human body.
"VasFluidics is quite different from the traditional fluidic systems. Channel walls of traditional devices are typically impermeable, and cannot work like real tissues to 'communicate' with fluids inside or outside the channel for fluid modulation," the author explained.
The reported technique combines 3D printing and self-assembly of soft materials. The research group prints one liquid within another immiscible liquid, assembling soft membranes on the liquid-liquid interface. Besides microfluidics-related research, the group also focuses on soft material assembly on the liquid interface. The theoretical and experimental basis of soft materials in their previous research paves the way for fabricating VasFluidic devices.
"VasFluidics has promising applications, especially for designing microtubule structures and bioinks. So it has great potential to be combined with cell engineering to develop artificial blood vessel models, which are expected to be used in biomedical applications, such as organ-on-chip and organoids," said a PhD student.
Another contributor to this research added: "Apart from the scientific merits and potential biomedical applications of this work, it also sparks our imagination. The vascular tissue of the human body, an efficient transport system, has been refined over millions of years of evolution. By demonstrating the potential of synthetic systems like VasFluidics to reconstruct vascular tissue, this research represents a substantial advancement in our efforts to mimic and harness the extraordinary capabilities of nature's most precise and efficient systems."
The team has been focusing on cutting-edge microfluidic techniques to push the envelope in precise (bio)liquid control and efficient (bio)liquid sample analysis. Despite their progress in microfluidics-assisted biomedical applications, the research team refused to just settle on the traditional setups. By exploring and realising the potential of microfluidics for more efficient biofluid processing and analysis, the team realises that new paradigms in designing and fabricating fluidic devices are needed.
"Our long-term goal is to utilise microfluidics to develop ultra-sensitive analysis of human body fluids, to assist precision medicine against diseases, and to benefit human health." The senior author said.
The author foresees that the VasFluidics system will pioneer biomimetic platforms with complex fluid manipulation. "Potential biomedical applications are boundless. Examples are in-vitro modelling of biological fluid mechanics, biomolecule synthesis, drug screening, and disease modelling in organ-on-chips," the author said.