Molecular cellular mechanism linked to microcephaly
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay, or NMD, is an evolutionarily conserved molecular mechanism in which potentially defective messenger RNAs, or mRNAs (genetic material that instructs the body on how to make proteins), are degraded. Disruption of the NMD pathway can lead to neurological disorders, immune diseases, cancers, and other pathologies. Mutations in human NMD regulators are seen in neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism and intellectual disability.
Why NMD mutations are enriched in neurodevelopmental disorders remains a mystery. Researchers published the work in the journal Neuron, that reveals the molecular cellular mechanism underlying NMD regulation of brain size and its dysregulation in causing microcephaly — a condition in which a baby’s head is much smaller than expected.
The team’s finding suggests that maintaining the neuronal NMD function is essential for early brain development to prevent microcephaly. According to the senior author, modulating NMD targets can be a potential treatment for microcephaly and other related neurodevelopmental diseases.
The study explains the functional roles of NMD in brain development and the underlying mechanistic action. It also demonstrates for the first time the link between mRNA decay regulation and brain size control. Additionally, it reveals the intricate connection between NMD and the most famous tumor suppressor gene, p53, suggesting possible new connections between NMD and cancer.
The senior author answers questions about the research:
Q: Why has it been a challenge to understand why NMD mutations are enriched in neurodevelopmental disorder?
A: As a surveillance mechanism, NMD targets defective mRNA arising from random mutations or RNA processing errors. This randomness is not expected to create idiosyncratic features of neurodevelopmental disorders associated with NMD factors. Furthermore, NMD occurs in all cell types and tissues, but the brain seems particularly vulnerable to NMD defects. Animal models of neural-specific NMD defects, followed by in-depth mechanistic investigation, are needed to understand why NMD mutations are enriched in neurodevelopmental disorder, which has not been conducted until now in part because of the complexity of brain development and the technical challenges of dissecting the functional NMD substrates.
Q: How did you identify the molecular cellular mechanism underlying NMD regulation of brain size and its dysregulation causing microcephaly?
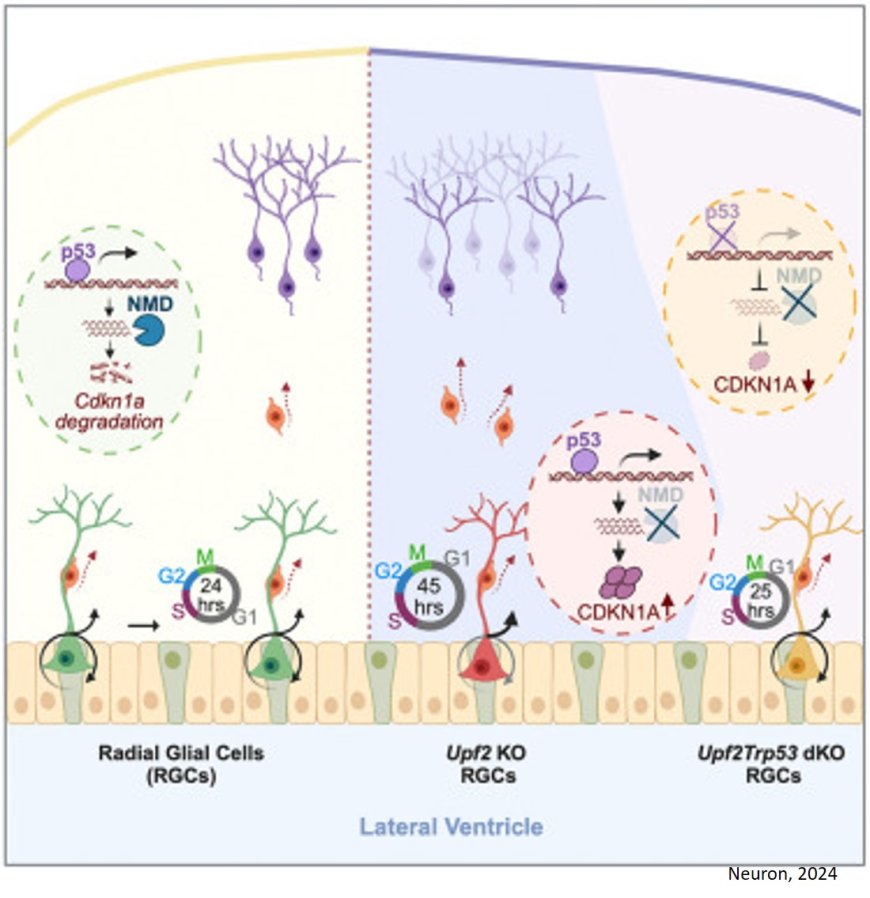
A: We generated various NMD deficiency animal models by knocking out a key NMD factor, Upf2, in different cell types and determined their phenotypic differences. We found NMD deficiency causes more impacts on the proliferative neural progenitors, which is consistent with the notion that NMD function is essential for early brain development and its mutations are enriched in neurodevelopmental disorders. Importantly, we showed NMD deficiency in progenitor cells cause microcephaly, a novel finding that links an NMD decay pathway to brain size control. To dissect the underlying mechanisms and determine functional NMD substrates causing these phenotypes, we applied cutting-edge technologies, including CRISPR screening, RNA-Seq, CLIP-seq, and single cell RNA-seq. Only through this integrative approach did we succeed in revealing the molecular underpinning.
Once we found the microcephaly phenotype, we used primary cell culture models to define the growth defects of Upf2 knockout, or Upf2KO, in neural progenitors. Next, we applied CRISPRi screening to identify genes whose perturbation can interfere with Upf2KO NPCs’ growth defect. Among hundreds of genes we screened, we identified a few candidates and followed on the top candidate, p53, which is well known to be a tumor suppressor gene that controls cell growth. Subsequently, we used various single cell approaches and transcriptomics technologies to determine precisely how NMD and p53 intersect in controlling cell growth.
The identification of p53 from the CRISPRi screen was a surprise to us because p53 is one of the most studied genes and many assume its genetic interactors are already identified and NMD has not made that list. Secondly, we showed deficiency in Trp53, a gene that encodes p53 (or TRP53), did not globally reverse the NMD inhibition to rescue the growth defects. Instead, our finding suggests that the TRP53 activity intersects with NMD pathway to regulate the neuronal progenitors’ cell cycle progression. This intersection represents a very small proportion of the NMD substrates, indicating that most NMD substrates have marginal functional impacts on cell growth.
Q: The study was done using mouse cells. Can we say the results would be replicated in human cells?
A: Yes. NMD pathway is evolutionarily conserved and the key factor we focused on in the study, UPF2, is conserved between human and mouse. Other molecular players we identified in this study are also conserved. Their regulatory rela