Human stem cell-derived GABAergic interneurons for epilepsy treatment
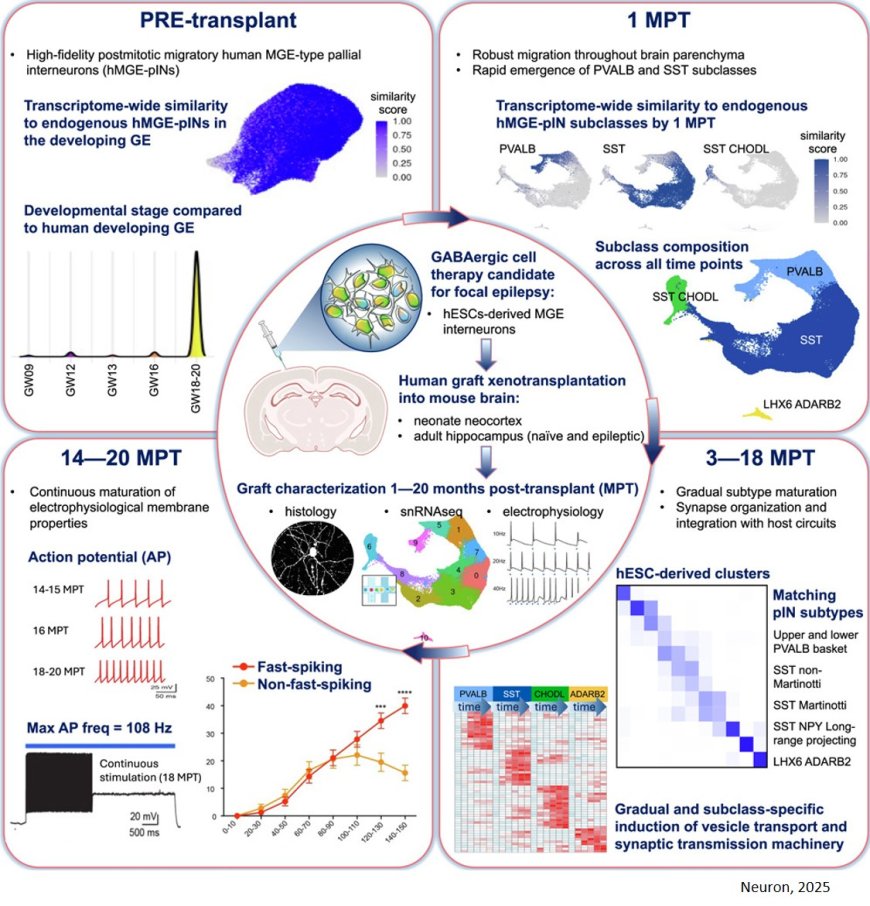
Inhibitory γ-aminobutyric acid (GABAergic) pallial interneurons (MGE-pINs) are essential regulators of cortical circuits, and their dysfunction is associated with neurological disorders.
For the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy, the researchers developed human MGE-pINs from pluripotent stem cells and describe the long-term properties of these human stem cell-derived GABAergic interneuron as a cell therapy candidate undergoing clinical evaluation for drug-resistant epilepsy.
Following transplantation into the brains of healthy or epileptic mice, grafted cells demonstrate exceptional purity, differentiation into authentic subtypes, integration with host circuitry, and gradual electrophysiological maturation.
They demonstrate that 97% of grafted cells developed into somatostatin (SST) and parvalbumin (PVALB) subtypes, including populations that exhibit selective vulnerability in Alzheimer’s disease.
https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(25)00468-4
https://sciencemission.com/Human-stem-cell-derived-GABAergic-interneuron-development