AI uncovers antiviral compounds using limited data!
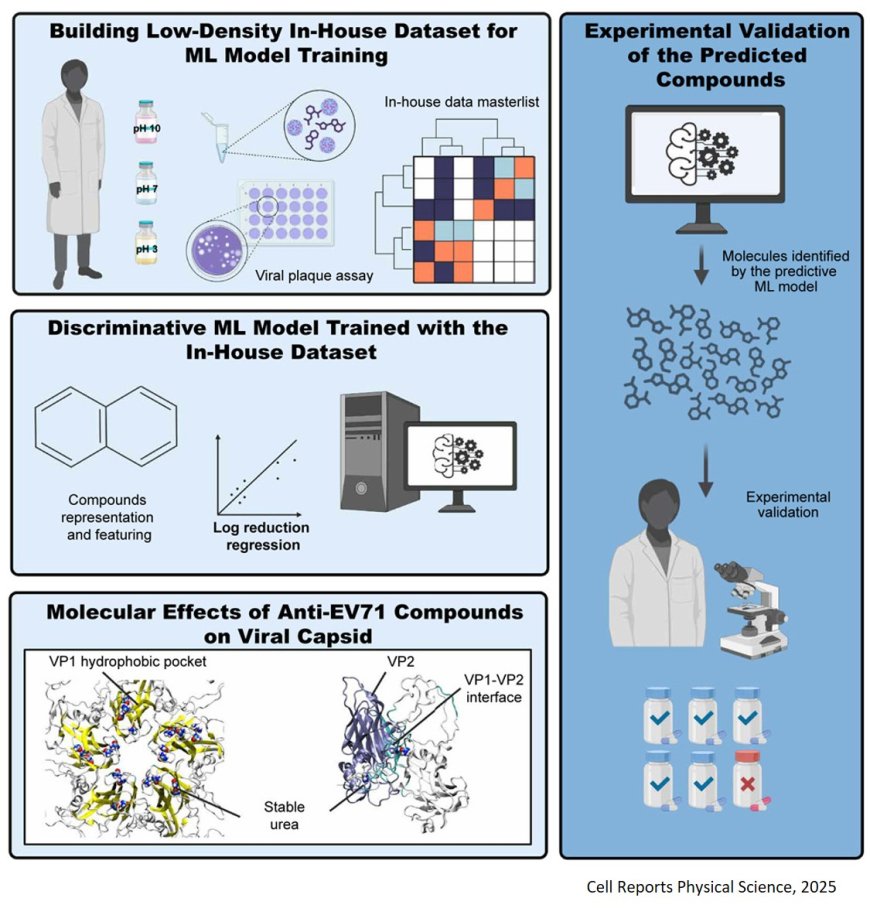
Artificial intelligence algorithms have now been combined with traditional laboratory methods to uncover promising drug leads against human enterovirus 71 (EV71), the pathogen behind most cases of hand, foot and mouth disease. The study, published in Cell Reports Physical Science showed that reliable antiviral predictions can be made even when only a modest amount of experimental data are available.
Using an initial panel of 36 small molecules, the investigators trained a machine learning model to spot certain shapes and chemical features that help stop viruses, scoring each compound’s likelihood of blocking EV71. The authors put their AI-chosen shortlist to the test: out of eight compounds, five successfully slowed the virus in cell experiments—about ten times more hits than traditional screening methods usually deliver.
“We are collapsing what used to be months of trial‑and‑error into days,” said the author. “The approach is especially powerful when time, budget or other constraints limit the amount of data you can generate up front.”
EV71 infections can escalate from mild rash and fever to severe neurological complications, particularly in children under seven and immunocompromised adults. No FDA-approved antivirals currently target the virus.
All five confirmed results were tested using computer simulations, which showed that they stuck to certain spots on the virus, findings which could help future researchers stop the virus from changing shape and entering cells.
“We see this as a template for rapid antiviral discovery,” added a study co-author. “Whether the next threat is another enterovirus, an emergent respiratory pathogen or a reemerging virus like polio, our AI-driven method shows that, even with limited data, machine learning can accelerate the development of effective solutions and drive a swift response to future outbreaks.”
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-physical-science/fulltext/S2666-3864(25)00153-5