Mechanism of action of Alzheimer’s genetic risk factor Bin1
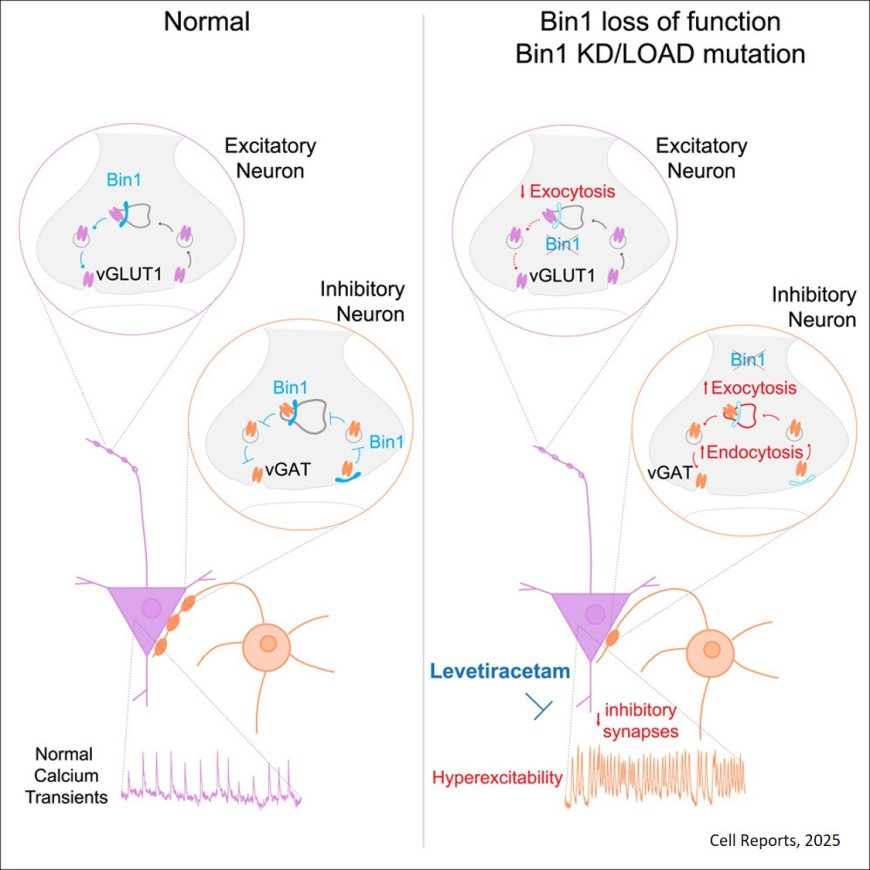
It is not clear how BIN1, a late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) risk gene disrupts synaptic function.
BIN1 is localized mainly in inhibitory synapses (vGAT positive). The researchers show that the Alzheimer’s risk gene BIN1 is critical for the stability of inhibitory synapses.
BIN1 deficiency accelerates the synaptic vesicle endocytic cycle, leading to synapse loss and neuronal hyperexcitability, a phenotype reversed by the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00776-4
https://sciencemission.com/Alzheimer%E2%80%99s-genetic-risk-factor-Bin1