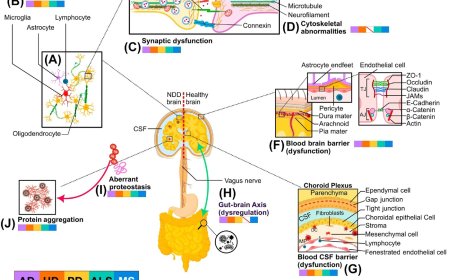
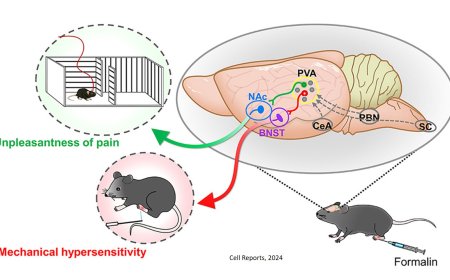
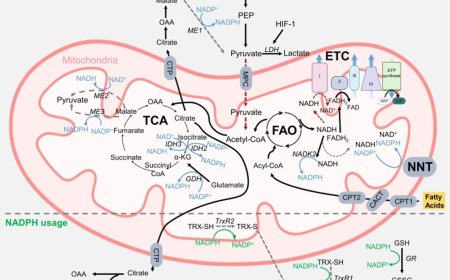
Interpreting non-coding variants using BRAIN-MAGNET

Although genetic variation using genome-wide assessment has been extensively carried out, interpretation of non-coding single nucleotide variants in both common and rare diseases is not established.
The researchers developed BRAIN-MAGNET, a convolutional neural network trained on 148,198 functionally tested non-coding regulatory elements and predicts enhancer activity directly from DNA sequence and identifies nucleotides essential for function.
This functional genomic atlas and BRAIN-MAGNET prioritize disease-relevant non-coding variants, advancing functional interpretation of the regulatory genome in neurodevelopment and neurological disease.