Guillain–Barré syndrome
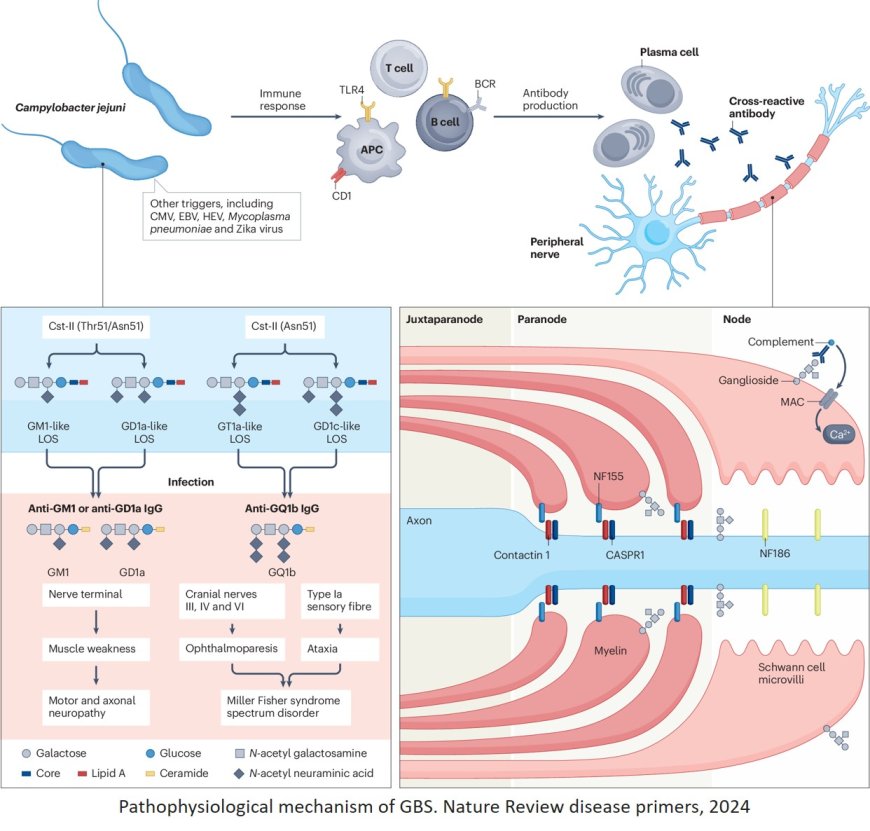
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a result of an aberrant immune response to an infection or other trigger that damages the peripheral nerves. GBS can cause rapidly progressive weakness and sensory deficits which may result in complete paralysis requiring mechanical ventilation.
Diagnosis of GBS is based on clinical features, supported by cerebrospinal fluid analysis and nerve conduction studies.
Effective treatments include plasma exchange and intravenous immunoglobulins. However, ~20% of patients who received treatment are unable to walk after 6 months and ~5% die as a consequence of GBS.
There is a lack of specific biomarkers to improve the diagnosis, monitor the disease activity, and predict the clinical course and outcome of GBS.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41572-024-00580-4
https://sciencemission.com/Guillain%E2%80%93Barr%C3%A9-syndrome