Gut microbiota-bile acid crosstalk contributes to nephropathy
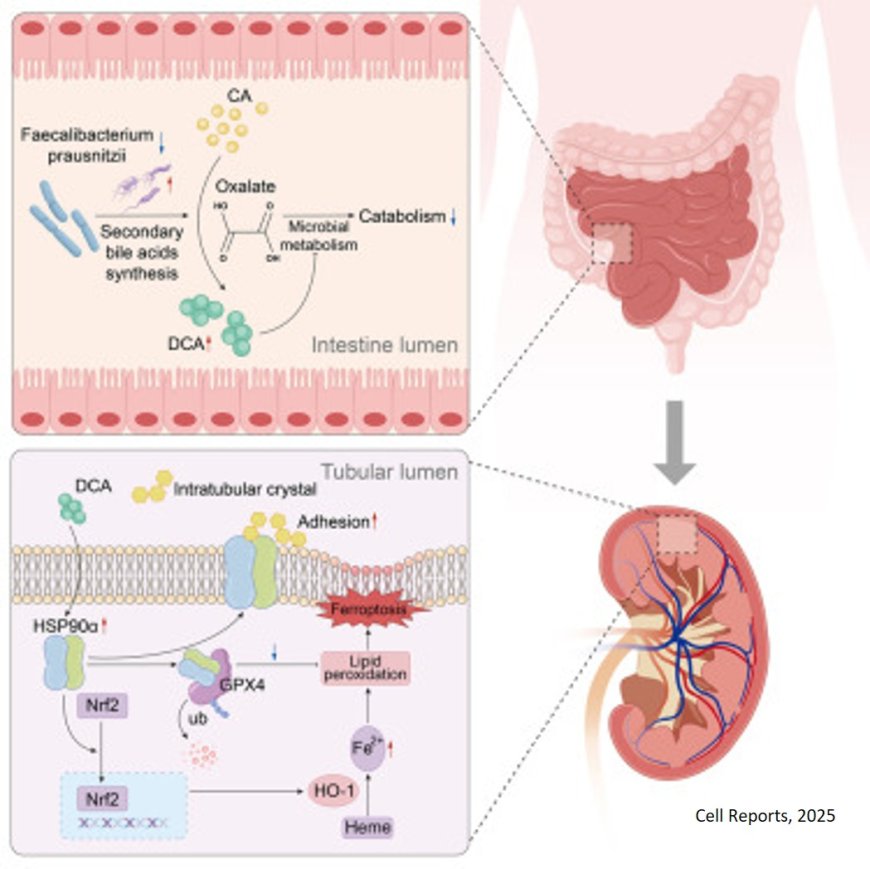
Calcium oxalate (CaOx) nephrolithiasis has been associated with gut microbiota but the precise mechanism is not well understood.
The authors observed CaOx nephrolithiasis patients with gut microbiota dysbiosis and an elevated level of deoxycholic acid (DCA), a secondary bile acid and diminished presence of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii.
The researchers also report that the decrease of F. prausnitzii in CaOx renal stone formers is accompanied by the increase of DCA. DCA impairs microbial oxalate catabolism and correlates positively with urinary oxalate excretion and stone burden and inversely with F. prausnitzii abundance.
Mechanistically, DCA promotes CaOx crystal deposition via HSP90α-mediated ferroptosis and crystal adhesion, revealing bile acid signaling as a potential therapeutic target.
Administration of F. prausnitzii to high-oxalate-diet mice alleviates renal CaOx crystal deposition by reducing DCA and secondary bile acid production.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00707-7
https://sciencemission.com/Gut-microbiota-bile-acid-crosstalk