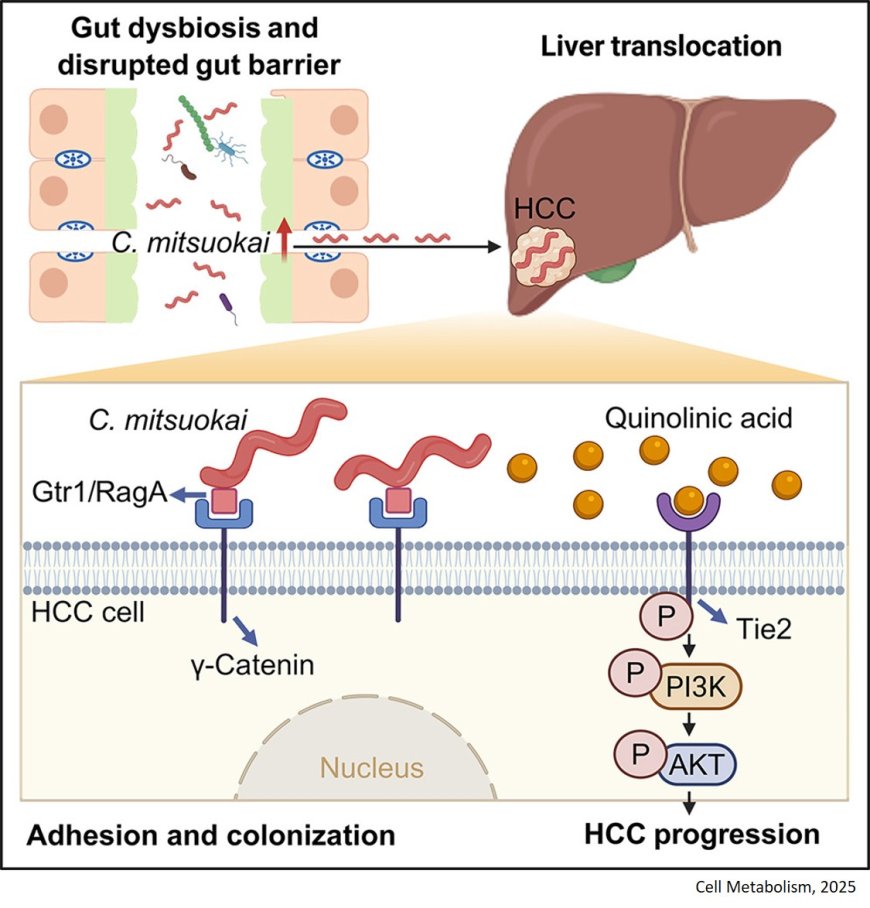
Mechanism of hepatocellular carcinogenesis from Catenibacterium mitsuokai
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from gut microbes is not well understood.
The researchers discovered enrichment of Catenibacterium in both the feces and tumors of patients with HCC. They also found HCC carcinogenesis acceleration from C. mitsuokai in both conventional and germ-free mice.
The researchers reveal that the gut bacterium Catenibacterium mitsuokai promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by disrupting the gut barrier, colonizing HCC cells via its surface protein Gtr1/RagA and receptor γ-catenin.
They also show that C. mitsuokai secrets quinolinic acid, which binds to TIE2 and activates the oncogenic PI3K/AKT pathway in HCC cells.
https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(25)00386-9
https://sciencemission.com/Catenibacterium-mitsuokai-promotes-HCC