Menin inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia
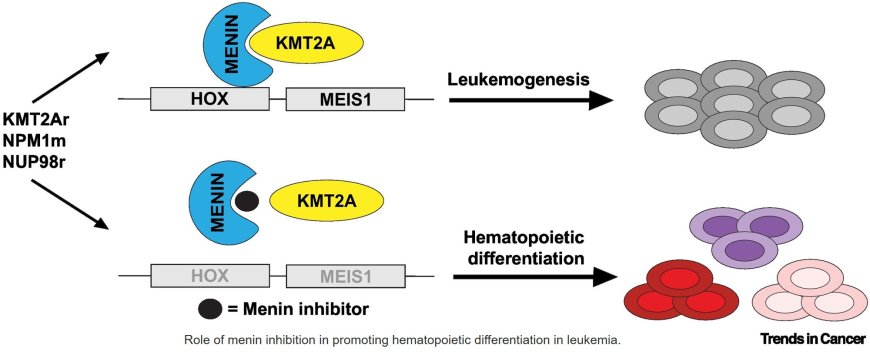
Menin promotes oncogenic transcriptional programs including canonical gene targets HOXA and MEIS1, particularly in KMT2A-rearranged, nucleophosmin 1–mutated, and NUP98-rearranged leukemia subsets.
Numerous menin inhibitors in development have conferred substantial clinical benefit as monotherapy and in combination with other antileukemic treatments in relapsed/refractory and newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia.
Notable toxicities of menin inhibitors, including differentiation syndrome and corrected QT interval prolongation, require close monitoring and early supportive care, as do other common adverse events such as cytopenias and infection.
Development of somatic mutations in MEN1 affecting the menin inhibitor binding site, epigenetic reactivation of menin target genes, and repression of noncanonical tumor suppressor transcriptional programs represent resistance mechanisms to menin inhibition.
https://www.cell.com/trends/cancer/fulltext/S2405-8033(25)00144-X