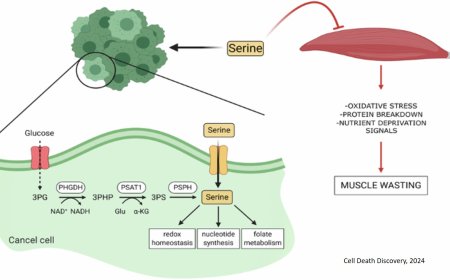
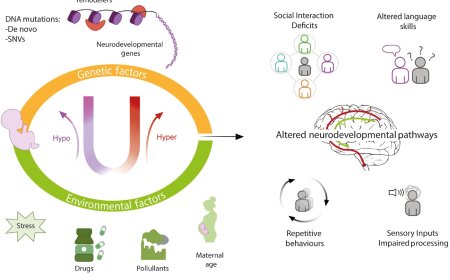
Mutated G proteins as drug targets
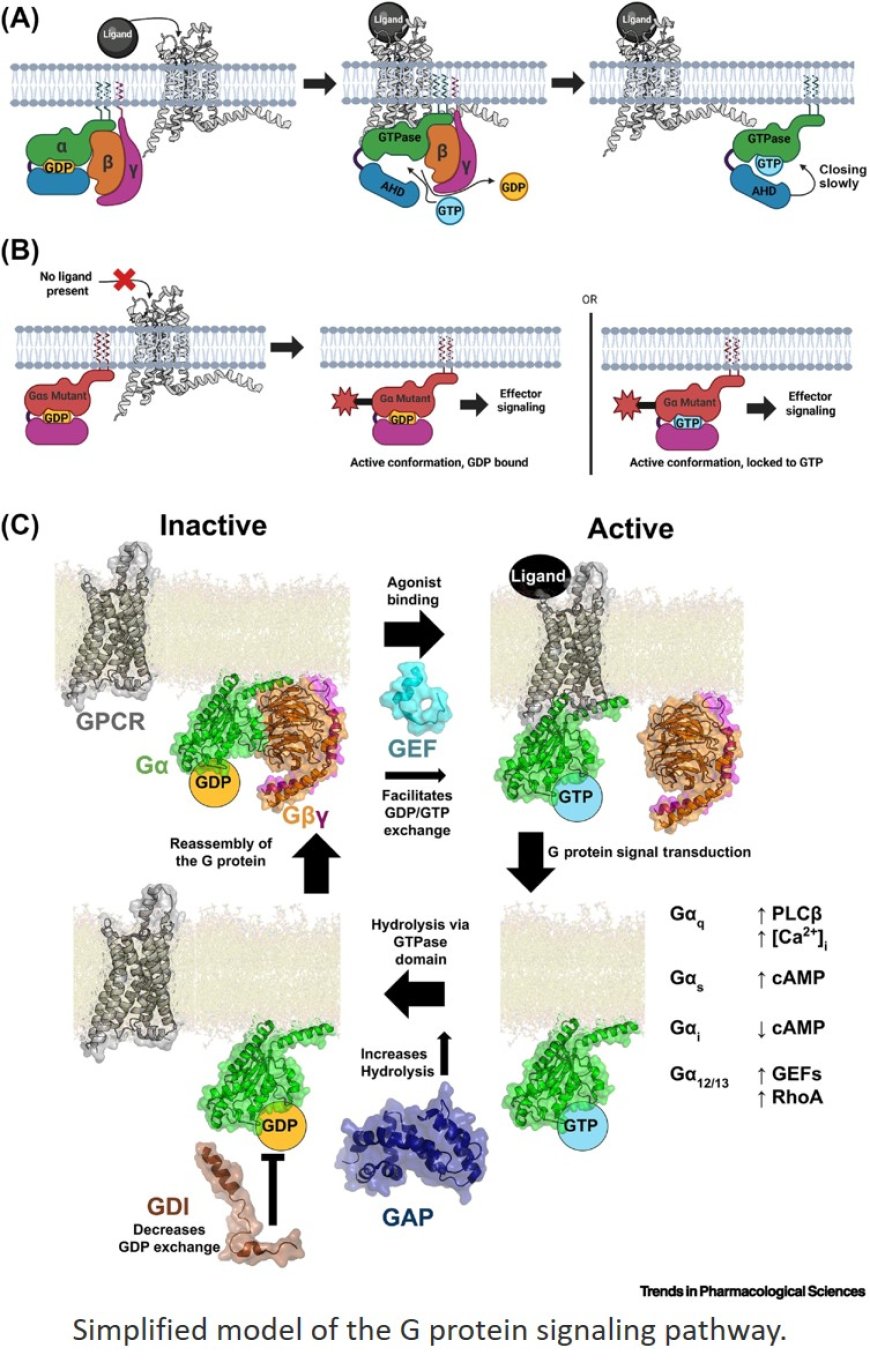
Although historically considered ‘undruggable,’ mutated G proteins, particularly Gαs, Gαi/o, and Gαq/11, are emerging as promising drug targets due to their direct involvement in human disease.
Most current modulators act on wildtype (WT) G proteins; however, a small number of compounds recently demonstrated selective activity against mutant Gαq/11, particularly in uveal melanoma.
Selectively targeting disease-associated G protein mutants offers a promising therapeutic strategy that circumvents the challenges of modulating WT proteins with broad physiological roles.
https://www.cell.com/trends/pharmacological-sciences/fulltext/S0165-6147(25)00145-2