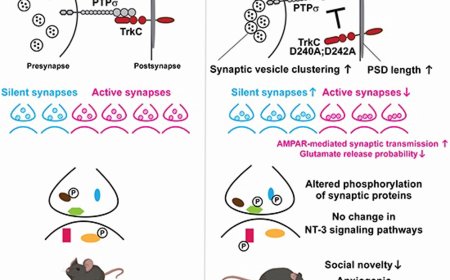
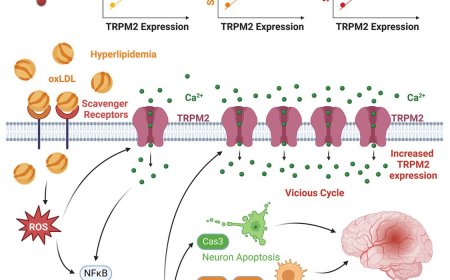
Neocortical somatostatin neuron diversity in cognition and learning
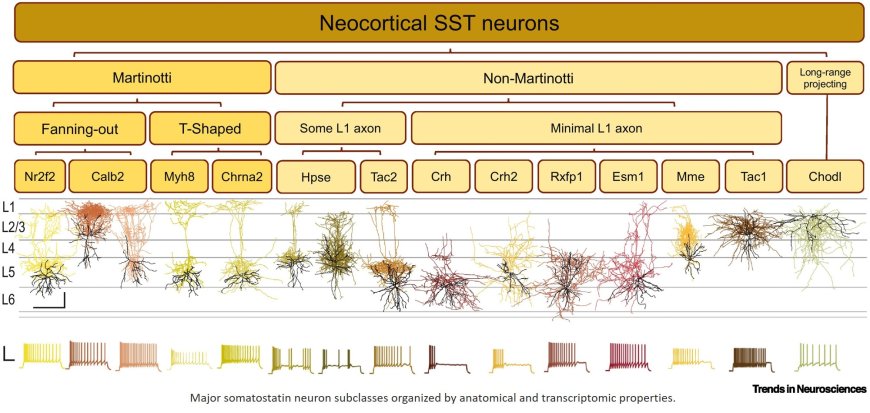
Recent studies in mice have identified dozens of transcriptomically-distinct subtypes of SST neurons in the neocortex. The functional implications of this diversity are ripe for exploration.
Brain state and behavior can modulate the activity of SST neurons, but effects are heterogeneous, based on age, subtype, brain area, and condition. Diverse response properties may be related to SST subtypes (e.g., Martinotti cells for arousal vs. nNos+ cells for sleep).
SST neurons are strongly implicated in cortical plasticity and learning, where SST activity is modulated by experience and chemogenetic manipulation of SST neurons can influence learning. Functional separation of SST subtypes in learning is an important goal in future studies.
https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/fulltext/S0166-2236(24)00249-2
https://sciencemission.com/Neocortical-somatostatin-neuron-diversity