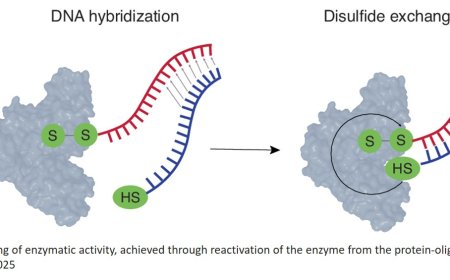
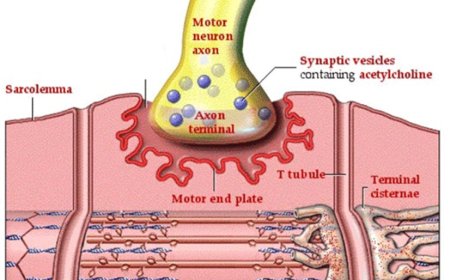
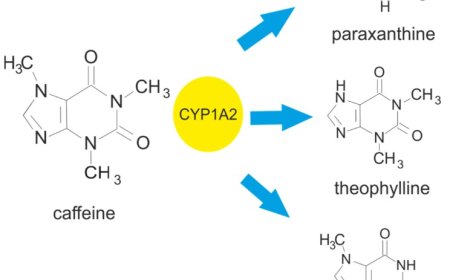
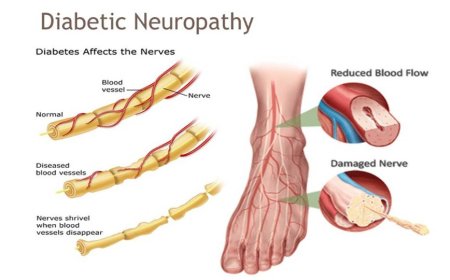
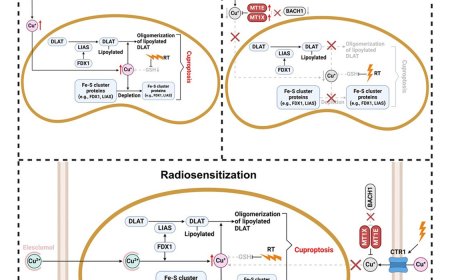
Protecting motor neurons against neuroinflammation
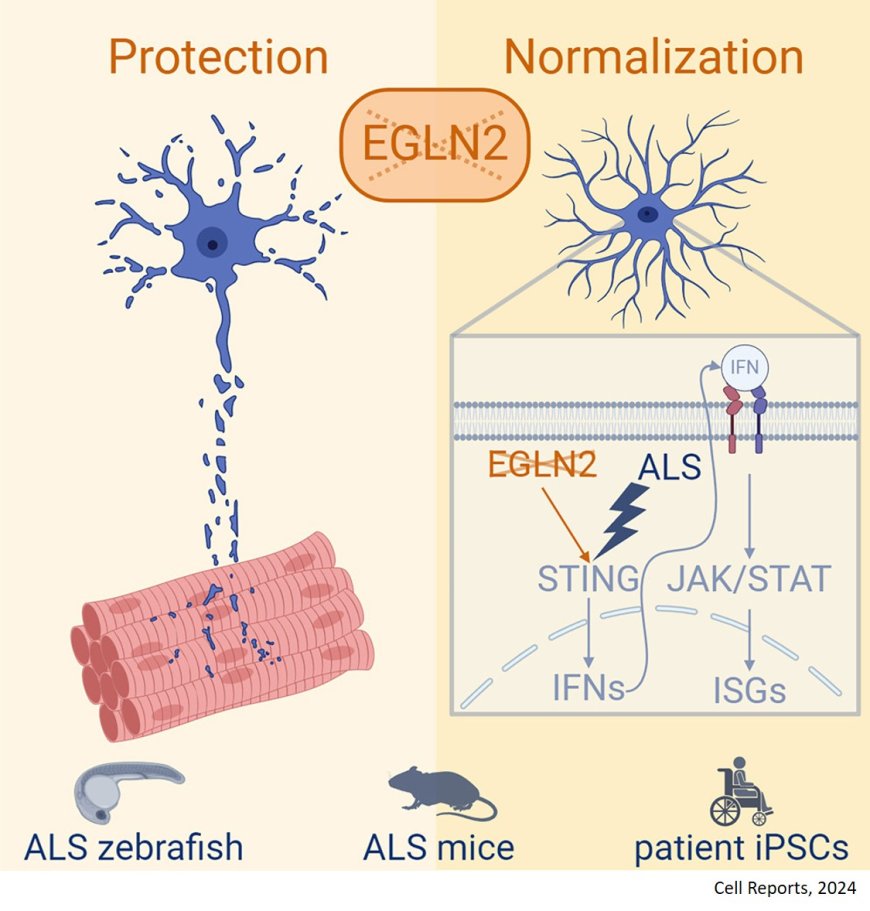
Energy metabolism dysregulation and neuroinflammation are associated with motor neuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The egl-9 family hypoxia-inducible factor (EGLN) enzymes, also known as prolyl hydroxylase domain (PHD) enzymes, are metabolic sensors regulating cellular inflammation and metabolism.
The researchers identify EGLN2 as an ALS target that, when downregulated, protects motor neurons and mitigates the ALS phenotype in ALS zebrafish and mice.
Using snRNA-seq and CRISPRCas9-edited patient iPSCs, they show that the downregulation of EGLN2 normalizes the STING-induced astrocytic interferon response in vivo in animal models.
The researchers found that the genetic deletion of EGLN2 restored the interferon response in patient induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived astrocytes, confirming the link between EGLN2 and astrocytic interferon signaling.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01070-2