Quality control of mitochondrial nucleoids
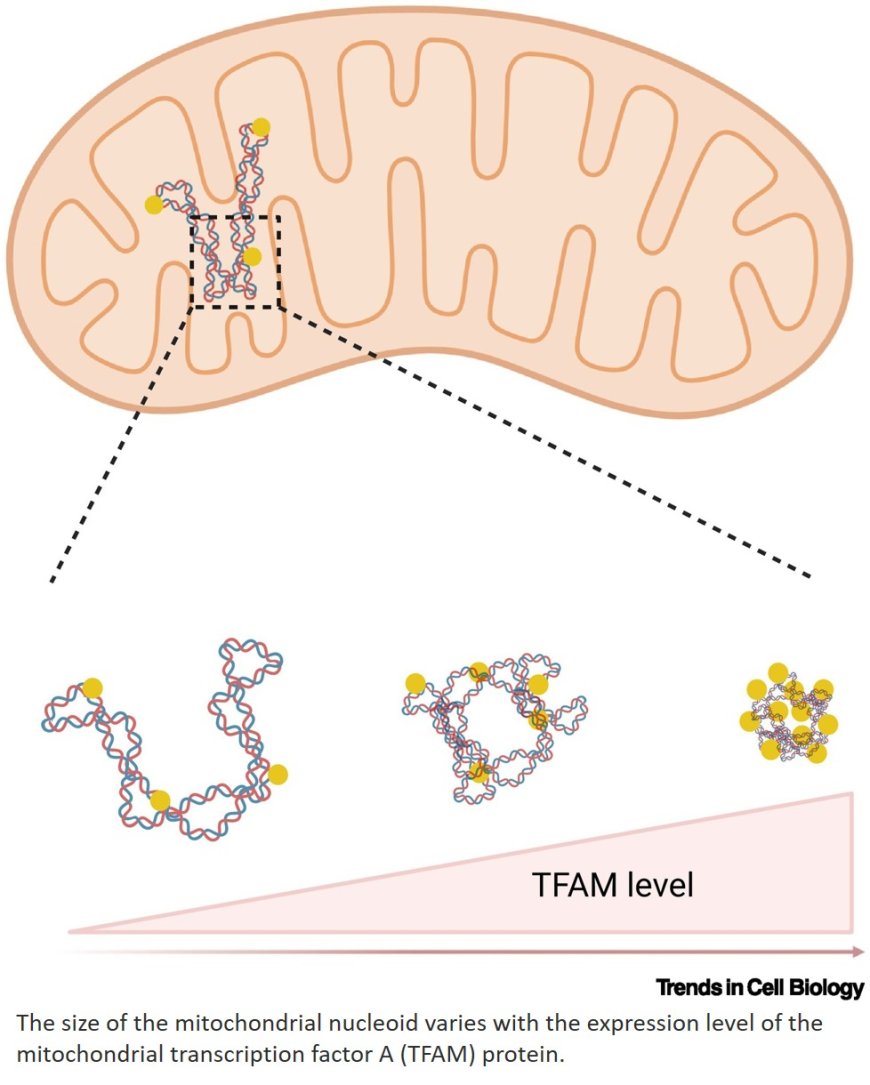
Mitochondrial nucleoids are complex structures containing mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and proteins like mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM), which maintains mtDNA packaging and regulates transcription through phase separation.
Under stress conditions, nucleoids can escape mitochondria through multiple pathways: mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening, BAX/ BAK pores, gasdermin proteins, and specialized vesicles [vesicles derived from the inner mitochondrial membrane (VDIMs), and mitochondrial-derived vesicles (MDVs)].
Quality control of nucleoids occurs through nucleoid-phagy (TFAMmediated) and mitophagy. Dysfunction in these processes leads to cytoplasmic accumulation of mtDNA, triggering inflammation via the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) pathway.
Abnormal nucleoid handling is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and aging-related conditions.
https://www.cell.com/trends/cell-biology/fulltext/S0962-8924(25)00039-X
https://sciencemission.com/Quality-control-of-mitochondrial-nucleoids