Regulation of glutamatergic signaling by tripartite circRNA/mRNA/miRNA interaction
The role of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in the cell physiology is not clearly defined yet.
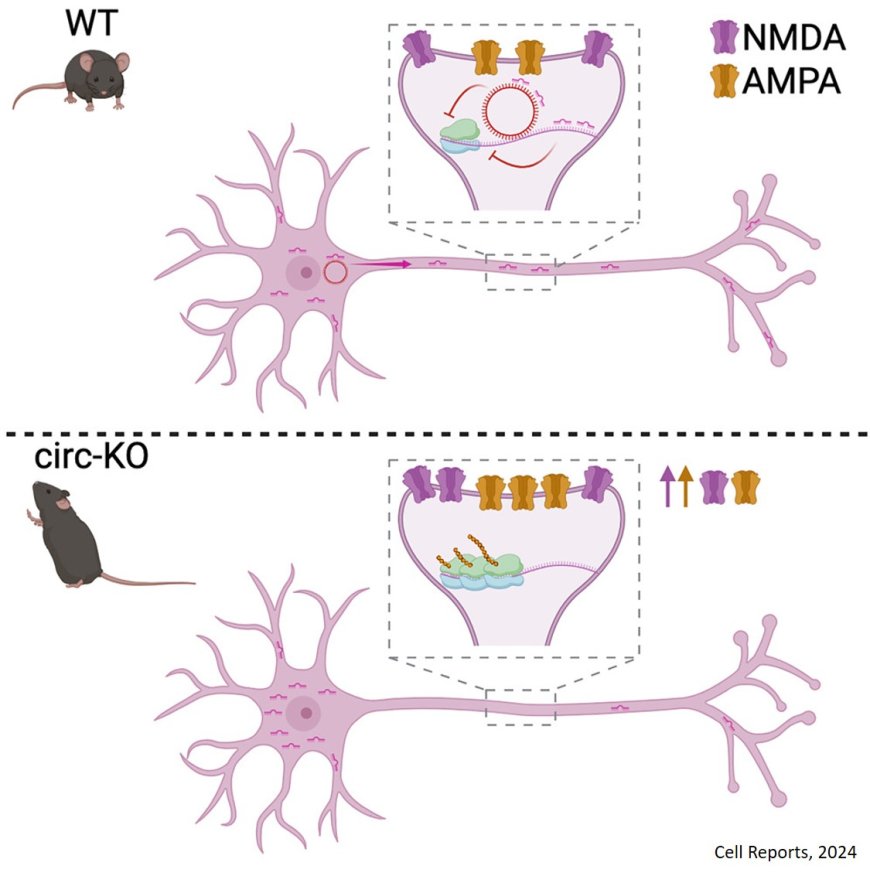
circDlc1(2), a circRNA highly expressed in the prefrontal cortex and striatum. The researchers report that the loss of circDlc1(2) in a KO mouse model upregulates glutamatergic genes, enhances synaptic transmission, and causes hyperactivity.
circDlc1(2) interacts with gluRNA and miR-130b-5p, synergizing with the latter to repress gluRNA expression.
It also spatially controls miR-130b-5p localization, highlighting an unprecedented gene regulation mechanism.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01117-3