Role of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p18 in mouse cortex lineage transition
Neurons and glia originate from neural stem cells (NSCs), but how the underlying differentiation transitions are regulated remains unclear.
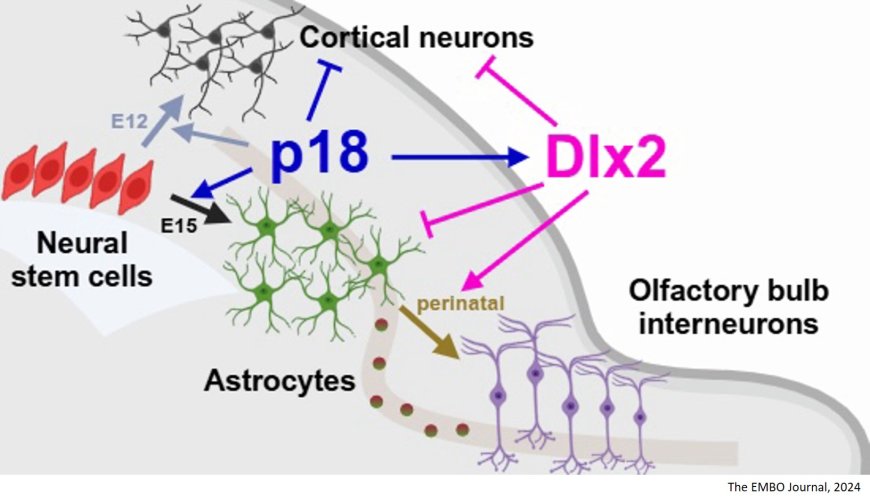
This study uncovers the importance of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p18 in promoting the developmental transition of NSCs into excitatory neurons, astrocytes, and olfactory bulb interneurons in the mouse dorsal cortex.
The researchers show that p18 modulates the generation of upper-layer cortical neurons and astrocytes.
They also demonstrate that p18 upregulates homeobox transcription factor Dlx2, which in turn induces olfactory bulb interneurons at the perinatal stage of development.
The suthors further show that p18 promotes transitions from NSCs to olfactory bulb interneurons via astrocytes within a single cell’s progeny.
https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.1038/s44318-024-00325-9