GCN2 acts as a glutamine sensor for mTORC1
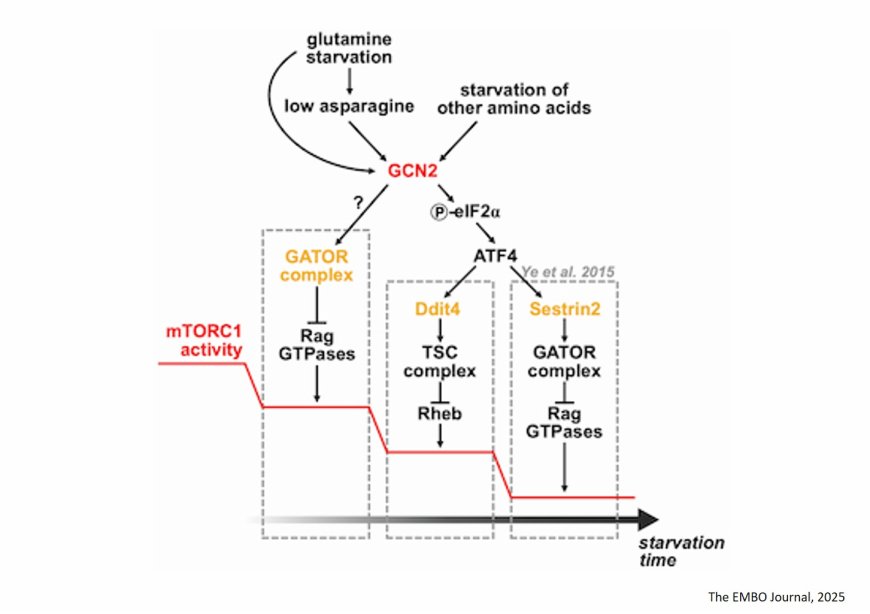
Availability of nutrients such as amino acids promote cell growth via mTORC1. During starvation, individual amino acid levels are thought to be relayed via distinct metabolic sensors, but how mTORC1 senses glutamine remains unclear.
This study finds that GCN2 kinase acts as a unifying module in suppression of mTORC1, and is activated by reduced levels of various distinct amino acids. Also, the study demonstrate that asparagine is the limiting metabolite sensed by mTORC1 during acute glutamine starvation.
The researchers show that glutamine removal inhibits mTORC1 via GCN2 through sequential mechanisms, both in Rag-dependent and Rag-independent manner. They also demonstrate that GCN2 function as an eIF2α kinase is not required for initial inhibition of mTORC1.
It was found that GCN2 inhibits mTORC1 also in response to starvation of multiple other amino acids and GCN2 and dedicated amino acid sensors act additively to control mTORC1.
https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.1038/s44318-025-00505-1