Repairing lysosomal damage!
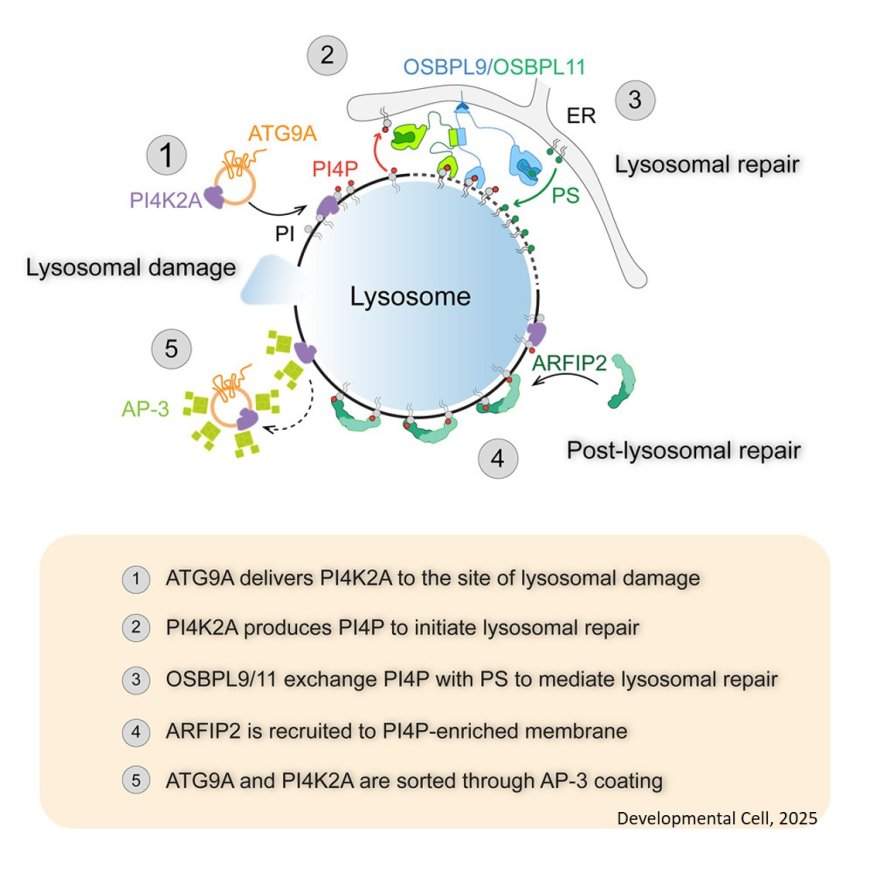
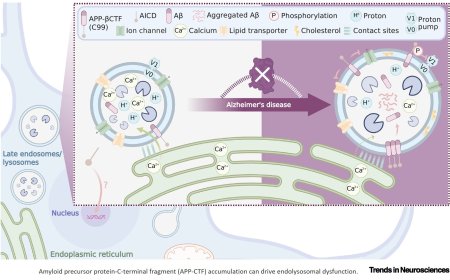
Preventing lysosome-dependent cell death following bacterial infection involves repair mechanism including endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-lysosome membrane contact sites, phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase-2a (PI4K2A), phosphatidylinositol-4 phosphate (PI4P), and oxysterol-binding protein-like proteins (OSBPLs) lipid transfer proteins.
However, the mechanism of PI4K2A delivery into damaged lysosomes during its repair is not well characterized.
The researchers discover that ATG9A vesicles deliver PI4K2A to damaged lysosomes, promoting PI4P production for membrane repair.
ARFIP2, a component of ATG9A vesicles, binds and sequesters PI4P on lysosomes, balancing OSBPL-dependent lipid transfer and promoting the retrieval of ATG9A vesicles through the recruitment of the adaptor protein complex-3 (AP-3), highlighting a finely tuned mechanism crucial for lysosomal integrity upon damage or infection.
https://www.cell.com/developmental-cell/fulltext/S1534-5807(25)00318-1