Suppressing necroptosis-induced colitis
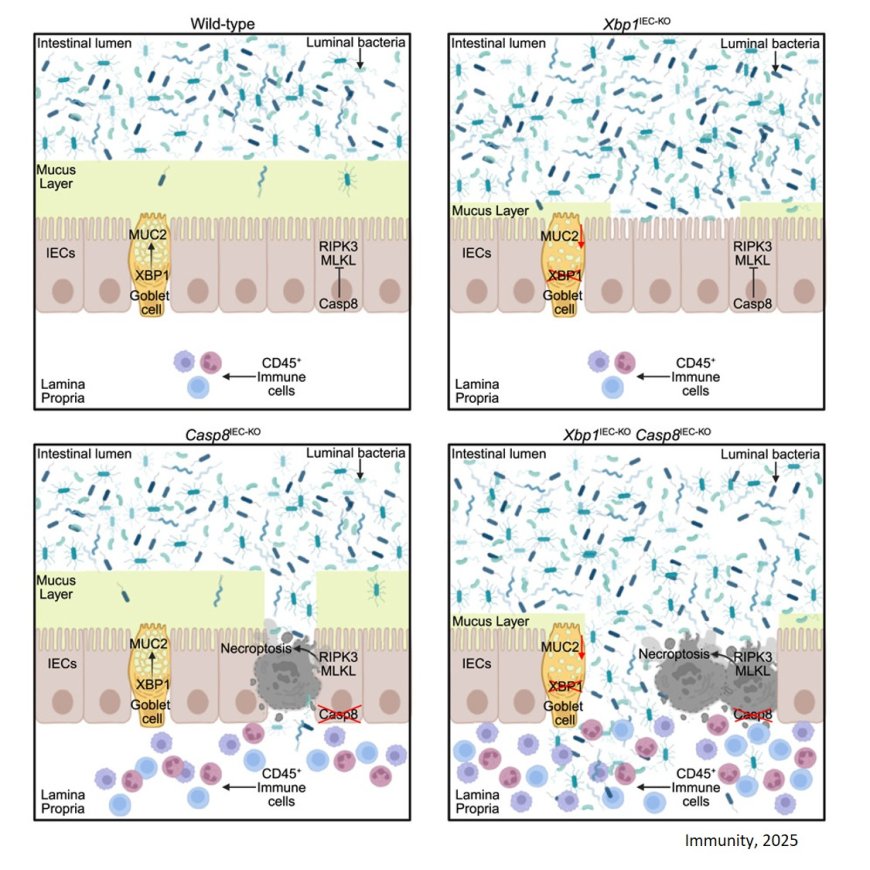
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial disease driven by combinations of susceptibility factors. IBD are associated with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and necroptosis but the potential crosstalk between these pathways is not well understood.
The researchers in this study demonstrate that how unfolded protein response transcription factor XBP1 deficiency impairs MUC2-mediated mucus barrier formation allowing bacteria to penetrate and reach the epithelial surface.
Diminished mucus formation synergizes with epithelial cell necroptosis to exacerbate colitis.
This work highlights how combined defects in epithelial integrity and the mucus layer drive chronic colon inflammation.
https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(25)00332-2
https://sciencemission.com/XBP1-suppresses-necroptosis-induced-colitis