The interoceptive origin of reinforcement learning
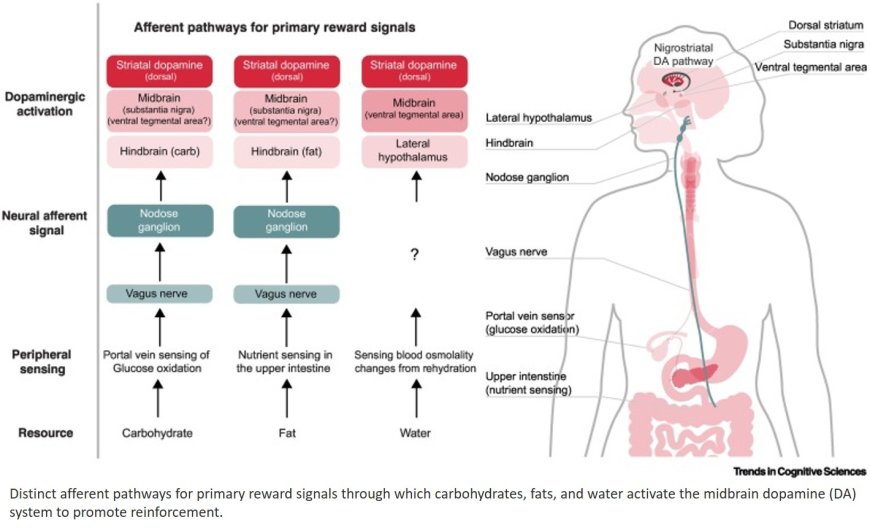
The reinforcing effects of food and fluids are driven by post-oral interoceptive primary reward signals, which reflect key physiological resources essential for sustaining life, such as energy, nutrients, and hydration.
Primary rewards are accompanied by a cascade of earlier signals – secondary and proxy rewards – that facilitate learning and prospective control rather than sustaining reinforcement.
Primary reward signals are dependent on internal states and goals.
The traditional reinforcement learning framework needs to be extended to address the generation of state-dependent reward signals and their interaction with reinforcement learning mechanisms within biological brains.
https://www.cell.com/trends/cognitive-sciences/fulltext/S1364-6613(25)00120-2