Mechanisms of post-stroke emotional disorders
The mechanisms behind post-stroke emotional disorders (PSEDs) remain unclear
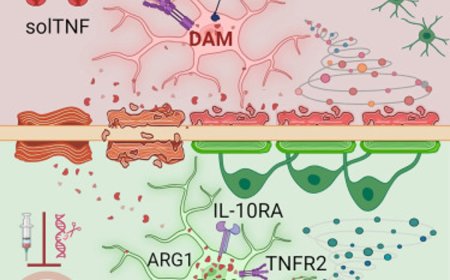
The researchers reveal that neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) serve as markers of post-stroke emotional disorders.
The infiltration of NETs into the brain parenchyma leads to the morphological and functional remodeling of astrocytes through the release of lipocalin 2 (Lcn2).
Early cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which inhibits Lcn2 release, significantly alleviates secondary emotional disorders following stroke.