The B7-H3 (CD276) pathway
B7-H3 is an immune checkpoint molecule and tumor-associated antigen that is highly expressed on multiple human tumor types.
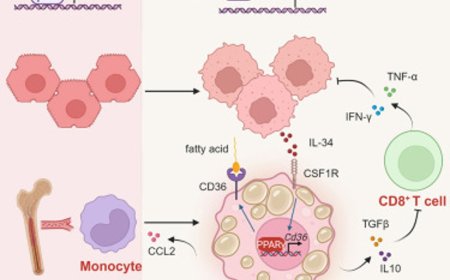
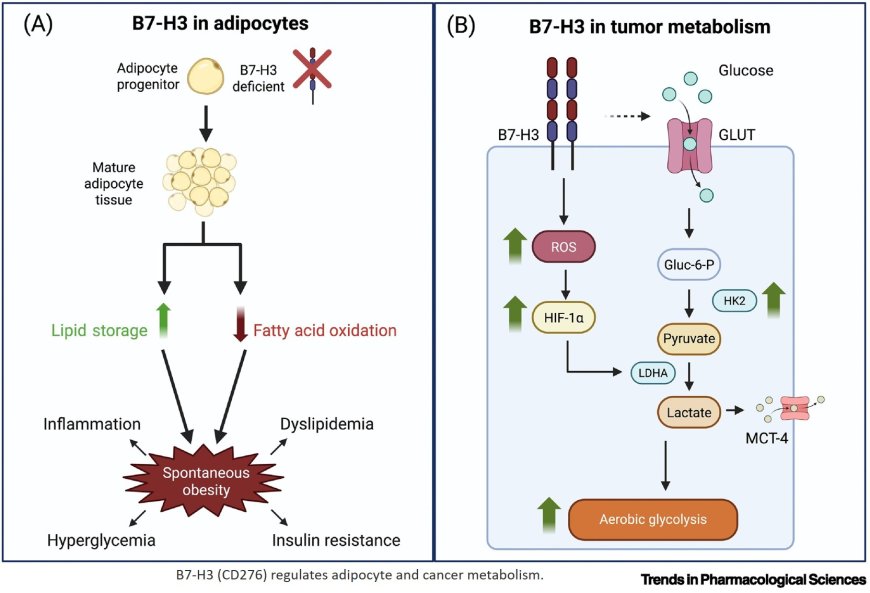
B7-H3 glycosylation is needed for its stability and function. B7-H3 is a metabolic regulator in adipocytes that plays a role in obesity development.
B7-H3 dimerization contributes to its intrinsic function in tumors.
Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting B7-H3 show tolerability and antitumor responses in Phase 1 and 2 clinical trials, and one is currently in a Phase 3 trial .
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells targeting B7-H3 are tolerated in Phase 1 clinical trials, and there are some indications of antitumor activity, but further data are not yet available.
https://www.cell.com/trends/pharmacological-sciences/fulltext/S0165-6147(25)00184-1