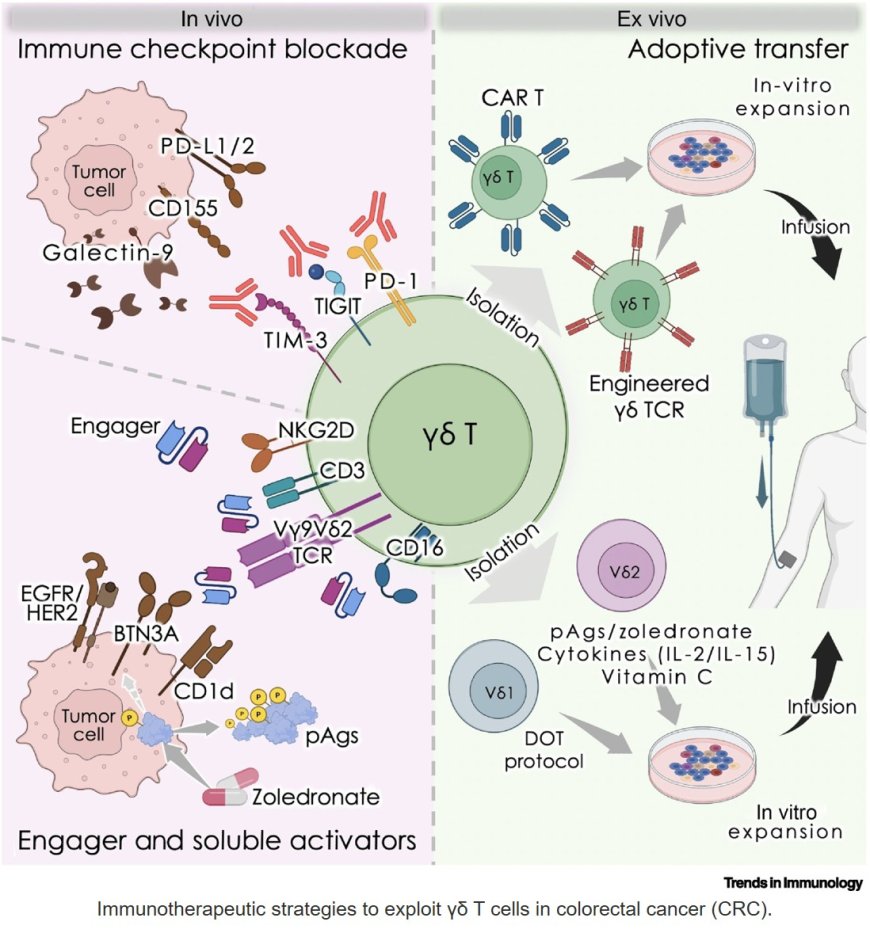
Colorectal cancer immunotherapies by targeting γδ T cells
Colorectal cancer (CRC) represents a major clinical issue, with growing rates in younger patients and few effective therapies.
γδ T cells in primary and metastatic CRC are highly heterogeneous and comprise functionally distinct subpopulations.
Some γδ T cell phenotypes protect against tumor progression and correlate with improved survival, suggesting that they have potential prognostic value.
γδ T cells respond to PD-1/PD-L1 axis inhibitors, particularly in HLA class Inegative CRC tumors.
PD-1+ γδ T cells show a profile of tumor reactive cells that can be reinvigorated via immune checkpoint blockade (ICB).
Combination strategies such as in vivo/ ex vivo activation and expansion, adoptive transfer, genetic engineering, and ICB are now being investigated to enhance γδ T cell specificity, persistence, and antitumor efficacy.
https://www.cell.com/trends/immunology/fulltext/S1471-4906(25)00308-4
https://sciencemission.com/Targeting-%CE%B3%CE%B4-T-cells-for-immunotherapies