How neuronal inflammasomes balance immunity, neuroinflammation, and homeostasis
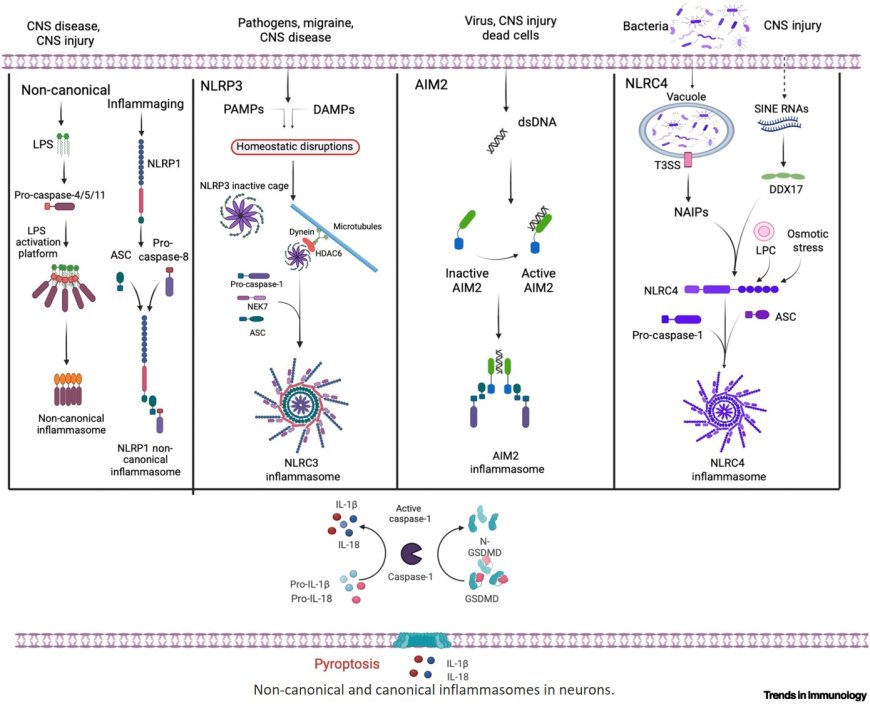
Neuronal inflammasomes drive neuroinflammation in infections, central nervous system (CNS) injury, and autoimmune disease.
Basal inflammasome activity is essential for brain homeostasis, including neuronal plasticity, axon pruning, synaptogenesis, and exosome trafficking.
Chronic or excessive neuronal inflammasome activation contributes to neurodegenerative and autoimmune pathologies.
Neurons actively sense and modulate immune signals, presenting new opportunities to target inflammasomes for CNS repair and inflammation control.
https://www.cell.com/trends/immunology/fulltext/S1471-4906(25)00306-0